The global economy is undergoing a massive transformation, powered by clean energy, electric vehicles, and digital technology. At the center of this transformation lies critical minerals such as lithium, cobalt, and rare earth elements. These resources are no longer seen just as raw materials; they have become strategic assets shaping the balance of power between nations.
The critical minerals race between China and the U.S. has emerged as one of the most important geopolitical contests of the 21st century. With China dominating much of the supply chain and the U.S. working hard to secure its independence, the stakes are high for industries ranging from renewable energy to defense systems.
This article dissects the five key drivers of the critical minerals race between China and the U.S., highlighting why these resources are now seen as a new form of geopolitical battleground.
1. Strategic Control of Supply Chains in the Critical Minerals Race Between China and the U.S.
Key Features:
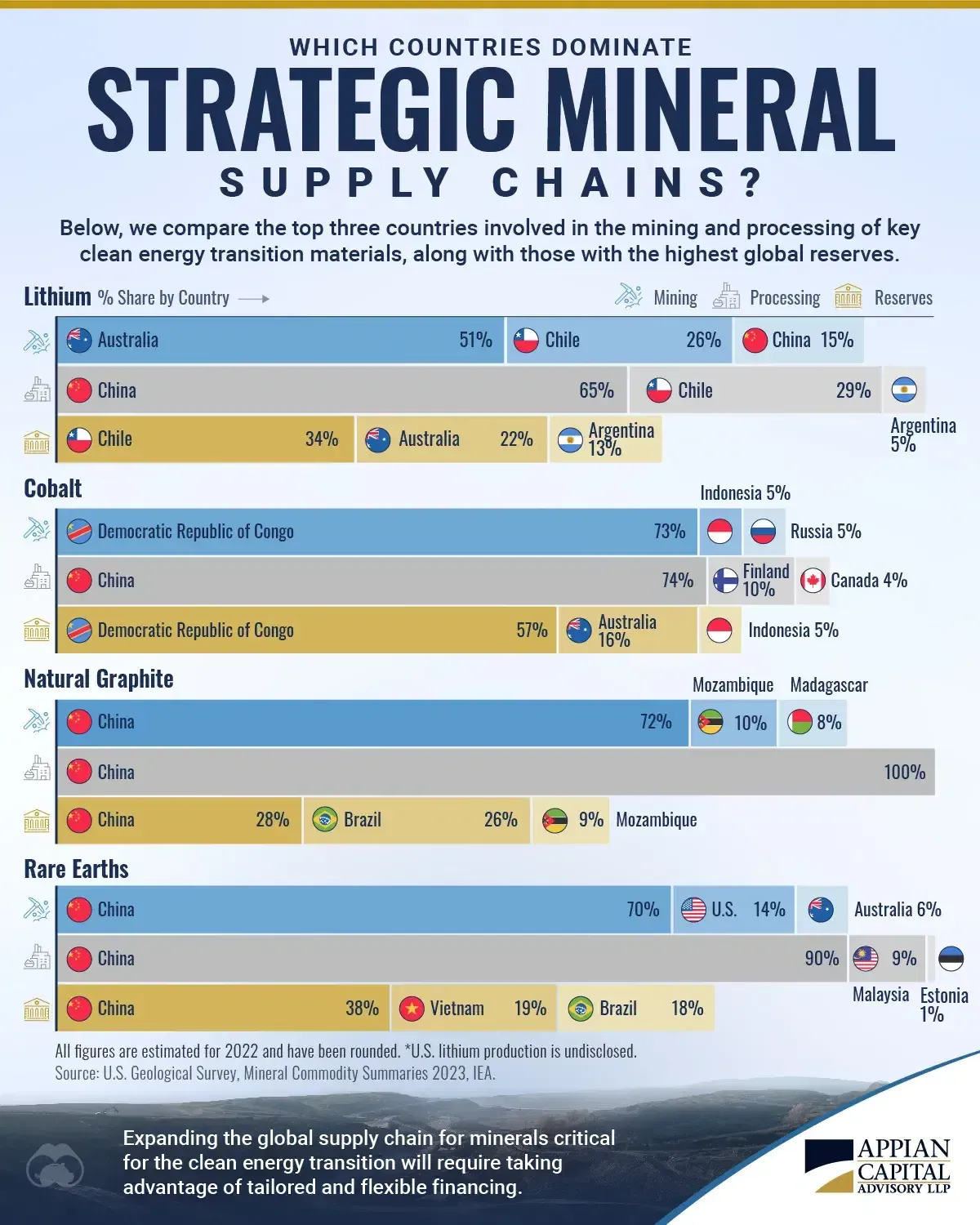
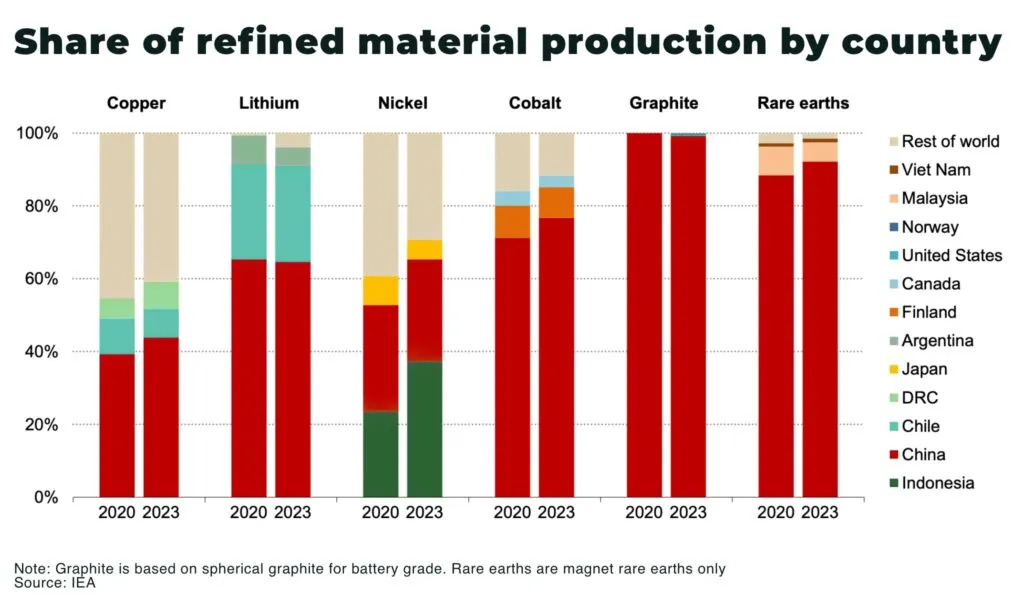
- China dominates more than 60% of global rare earth production.
- The U.S. depends heavily on imports for critical minerals like lithium and cobalt.
- Supply chains are vulnerable to geopolitical tensions and trade restrictions.
- Efforts are being made to diversify supply and reduce dependency.
The most significant factor driving the critical minerals race between China and the U.S. is control over supply chains. China has successfully built an integrated system of mining, refining, and processing critical minerals, allowing it to dominate global markets.
By contrast, the U.S. has strong demand but limited domestic production, leaving it reliant on foreign imports. This imbalance has raised serious concerns in Washington about national security and economic stability. To counter this, the U.S. is investing in domestic mining projects and building strategic alliances with countries like Australia and Canada.
2. Energy Transition Needs in the Critical Minerals Race Between China and the U.S.
Key Features
- Lithium and cobalt are essential for electric vehicle (EV) batteries.
- Rare earths are vital for wind turbines, solar panels, and energy storage.
- Demand for these minerals is expected to triple by 2035.
- Both nations are prioritizing clean energy technologies.
The shift toward renewable energy and decarbonization has accelerated the critical minerals race between China and the U.S.. Electric vehicles and renewable energy systems cannot function without stable supplies of lithium, cobalt, and rare earths.
China has positioned itself as a leader in renewable technologies, supported by its mineral advantage. The U.S., however, is pushing for a stronger role in clean energy innovation and manufacturing, recognizing that its success depends on reducing reliance on foreign-controlled mineral supplies.
3. National Security Concerns in the Critical Minerals Race Between China and the U.S.
Key Features
- Rare earths are used in fighter jets, missiles, and defense systems.
- Supply disruptions could weaken military readiness.
- China has previously threatened export restrictions during trade disputes.
- U.S. defense strategies now include mineral independence.
National security is another driver behind the critical minerals race between China and the U.S.. Rare earth elements are essential for producing advanced military technologies. A shortage or trade restriction could directly impact the U.S. military and its allies.
China has not hesitated to use its mineral dominance as leverage during past disputes. This possibility has prompted Washington to classify critical minerals as strategic assets and fund alternative supply chains. Defense contractors and government agencies are also exploring recycling and substitution technologies to reduce risks.
4. Technological Innovation and Industrial Competition in the Critical Minerals Race Between China and the U.S.
Key Features
- Minerals support industries like semiconductors, AI, and 5G networks.
- China’s industrial policies ensure steady mineral access for tech giants.
- The U.S. is investing in research and recycling technologies.
- Innovation depends on affordable and reliable mineral supplies.
The critical minerals race between China and the U.S. also reflects broader competition in technology and industry. From smartphones to satellites, critical minerals are the backbone of modern electronics.
China’s dominance has given its companies a competitive advantage in production and pricing. To level the playing field, the U.S. is encouraging domestic innovation, particularly in battery recycling and alternative materials. This technological rivalry is not just about clean energy—it is about who will lead the next generation of industrial revolutions.
5. Geopolitical Alliances and Global Influence in the Critical Minerals Race Between China and the U.S.
Key Features
- China has invested heavily in Africa and South America’s mineral sectors.
- The U.S. is building alliances with Canada, Australia, and the EU.
- Developing countries are key battlegrounds for influence.
- Control of resources impacts global trade power.
The critical minerals race between China and the U.S. extends far beyond their borders. Both nations are competing for influence in resource-rich regions. China has established strong ties with African and Latin American nations, where much of the world’s cobalt and lithium reserves are found.
Meanwhile, the U.S. is working with allies to create secure, transparent, and ethical supply chains. These alliances are designed to counterbalance China’s dominance and ensure that democratic nations maintain access to critical resources in the years ahead.
Conclusion – 5 Drivers of the Critical Minerals Race Between China and the U.S.

The critical minerals race between China and the U.S. is reshaping global geopolitics. What once seemed like simple raw materials are now central to economic strength, technological leadership, and national security.
From supply chain control to renewable energy transitions, national defense, industrial innovation, and global alliances, the race is about far more than resources—it is about the future of power itself.
The world will continue to watch how the U.S. reduces its dependency while China works to maintain its advantage. One thing is certain: critical minerals will remain at the heart of global competition for decades to come.
Table: Overview of the Critical Minerals Race Between China and the U.S.
| Driver | Key Resources | China’s Position | U.S. Position | Global Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Chains | Lithium, Rare Earths, Cobalt | Dominates mining and refining | Relies on imports, building alliances | Vulnerable to disruption |
| Energy Transition | Lithium, Cobalt, Rare Earths | Leads EV battery and renewable tech | Expanding domestic projects | Growing demand for clean energy |
| National Security | Rare Earths | Export control leverage | Military dependence on imports | Defense readiness at risk |
| Industrial Tech | Rare Earths, Lithium | Strong manufacturing base | Investing in recycling, R&D | Drives innovation globally |
| Geopolitics | Lithium, Cobalt | Africa & Latin America ties | Alliances with Canada, EU, Australia | Shapes global influence |
FAQs on 5 Drivers of the Critical Minerals Race Between China and the U.S.
1. What are critical minerals?
Critical minerals are essential resources like lithium, cobalt, and rare earths that are vital for energy, technology, and defense.
2. Why is China leading in critical minerals?
China has invested in mining, refining, and global supply chains, giving it dominance in production and processing.
3. Why is the U.S. concerned about critical minerals?
The U.S. relies on imports, creating risks for its economy, energy security, and defense readiness.
4. Which industries depend on critical minerals?
Industries include electric vehicles, renewable energy, defense, electronics, and aerospace.
5. How do critical minerals impact national security?
Rare earths are used in fighter jets, missiles, and communications systems, making them vital for military strength.
6. What is the role of lithium in the critical minerals race?
Lithium is crucial for EV batteries, making it a key resource in the U.S.-China competition.
7. Can the U.S. reduce its dependency on China?
Yes, through domestic mining, recycling, and alliances with resource-rich allies.
8. How do critical minerals affect clean energy?
They are the building blocks of batteries, solar panels, and wind turbines needed for renewable power.
9. What regions are most important for critical minerals?
Africa and South America hold large reserves of lithium and cobalt, making them central to global supply chains.
10. What is the future of the critical minerals race?
The competition will intensify as demand for clean energy and advanced technology continues to grow.








