U.S.–China relations have always been complex, filled with cooperation in some areas and sharp disputes in others. This year, the rivalry has deepened, shaping global trade, security, and technology policies. From economic disagreements to territorial disputes, the two powers continue to test each other’s influence across the world.
The 5 big disputes defining U.S.–China relations this year highlight not just bilateral tensions but also their impact on international stability. Issues such as Taiwan, trade wars, the race for artificial intelligence and advanced technology, territorial claims in the South China Sea, and economic sanctions are at the forefront. Each of these disputes influences global supply chains, diplomatic relations, and strategic alliances.
Understanding these disputes is critical for policymakers, businesses, and ordinary citizens who are directly affected by shifts in global markets and security environments. Let’s break down the five major points shaping the U.S.–China rivalry in 2025.
1. Taiwan: The Core of U.S.–China Tensions
Key Features:
- Taiwan remains the most sensitive and high-stakes dispute.
- The U.S. continues to provide military and diplomatic support to Taiwan.
- China views Taiwan as a breakaway province that must be reunified.
- Frequent military drills in the Taiwan Strait have increased risks of confrontation.
- The global semiconductor industry depends heavily on Taiwan.
Taiwan sits at the heart of U.S.–China relations. For Beijing, reunification with Taiwan is a non-negotiable goal, while Washington sees Taiwan as a crucial democratic partner in Asia. Military activities around the Taiwan Strait have intensified, raising concerns of potential conflict.
Taiwan’s importance extends beyond politics. As the global leader in semiconductor production, its stability directly impacts international supply chains. U.S. support for Taiwan, including arms sales and official visits, has been met with sharp criticism and countermeasures from China. This issue remains the single greatest flashpoint in the bilateral relationship.
2. Trade Wars and Tariffs
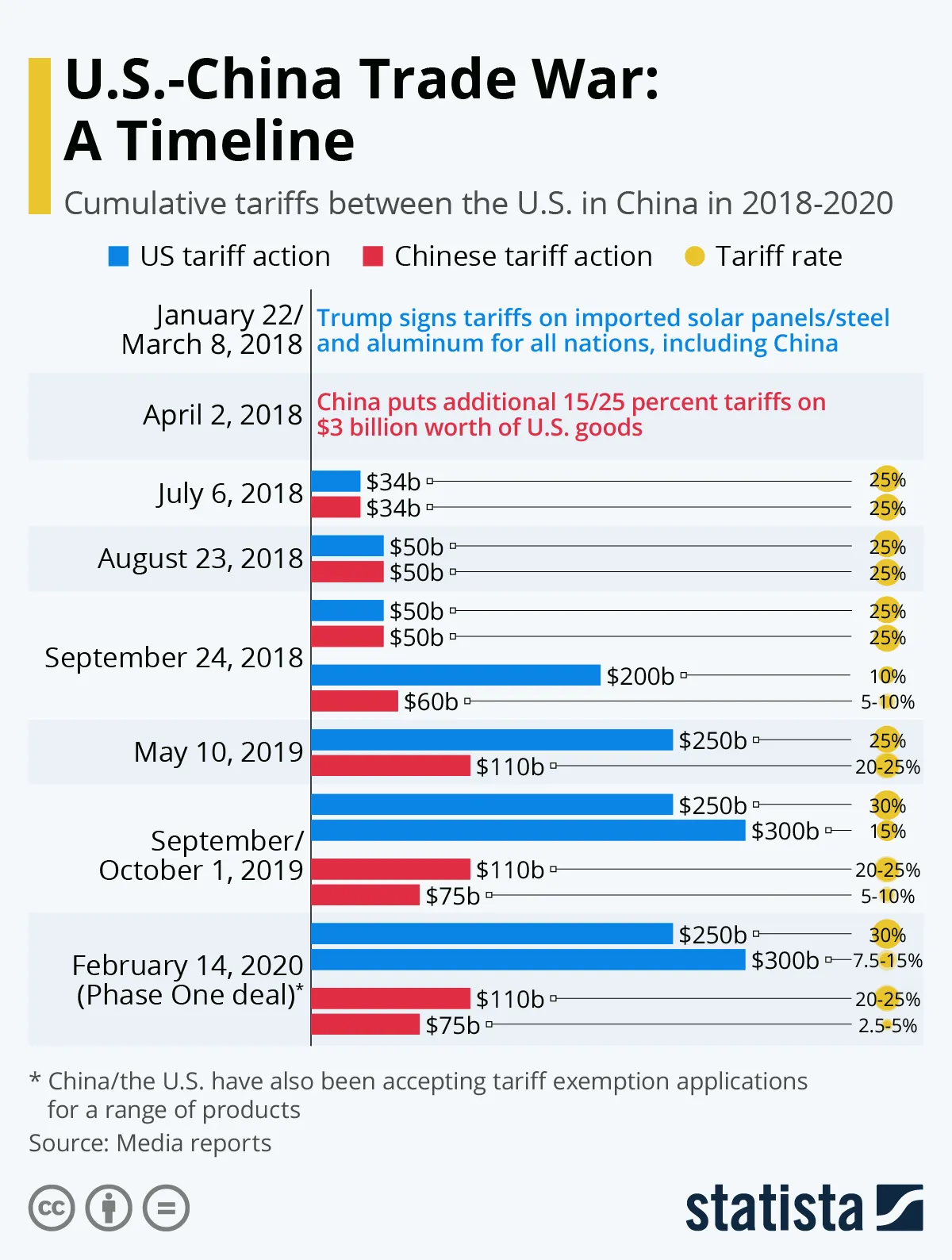
Key Features:
- The U.S. has imposed tariffs on Chinese goods to counter unfair trade practices.
- China has retaliated with tariffs on American exports.
- Supply chains are shifting as companies diversify away from China.
- Global inflationary pressures are linked to U.S.–China trade disputes.
- Both countries accuse each other of economic coercion.
The trade wars between the United States and China continue to disrupt global markets. Washington argues that Beijing engages in unfair trade practices, subsidies, and intellectual property theft. In response, tariffs have been used as leverage, but China has answered with its own countermeasures.
The result has been a shift in global trade patterns. Many companies are moving manufacturing operations to countries like Vietnam, India, and Mexico to avoid tariff risks. However, the economic ripple effects still impact consumers worldwide. The trade war shows no sign of resolution, as both sides prioritize protecting domestic industries and reducing dependency on one another.
3. AI and Technology Race
Key Features:
- The U.S. and China are competing for dominance in artificial intelligence.
- Washington has restricted exports of advanced semiconductors to China.
- China is investing heavily in domestic chip-making and AI research.
- Both nations see AI as crucial for military and economic power.
- The tech rivalry extends to 5G, quantum computing, and cybersecurity.
Technology has become the new battlefield in U.S.–China relations. The United States is determined to limit China’s access to advanced semiconductors, which are essential for artificial intelligence, supercomputing, and military applications. Export controls and restrictions on American companies working with Chinese tech giants have escalated tensions.
China, on the other hand, has doubled down on self-sufficiency. With massive government investments in AI research, chip production, and digital infrastructure, Beijing aims to lead in future technologies. This rivalry has global consequences, as other nations must choose between U.S.-aligned or China-aligned technology ecosystems.
4. South China Sea Disputes
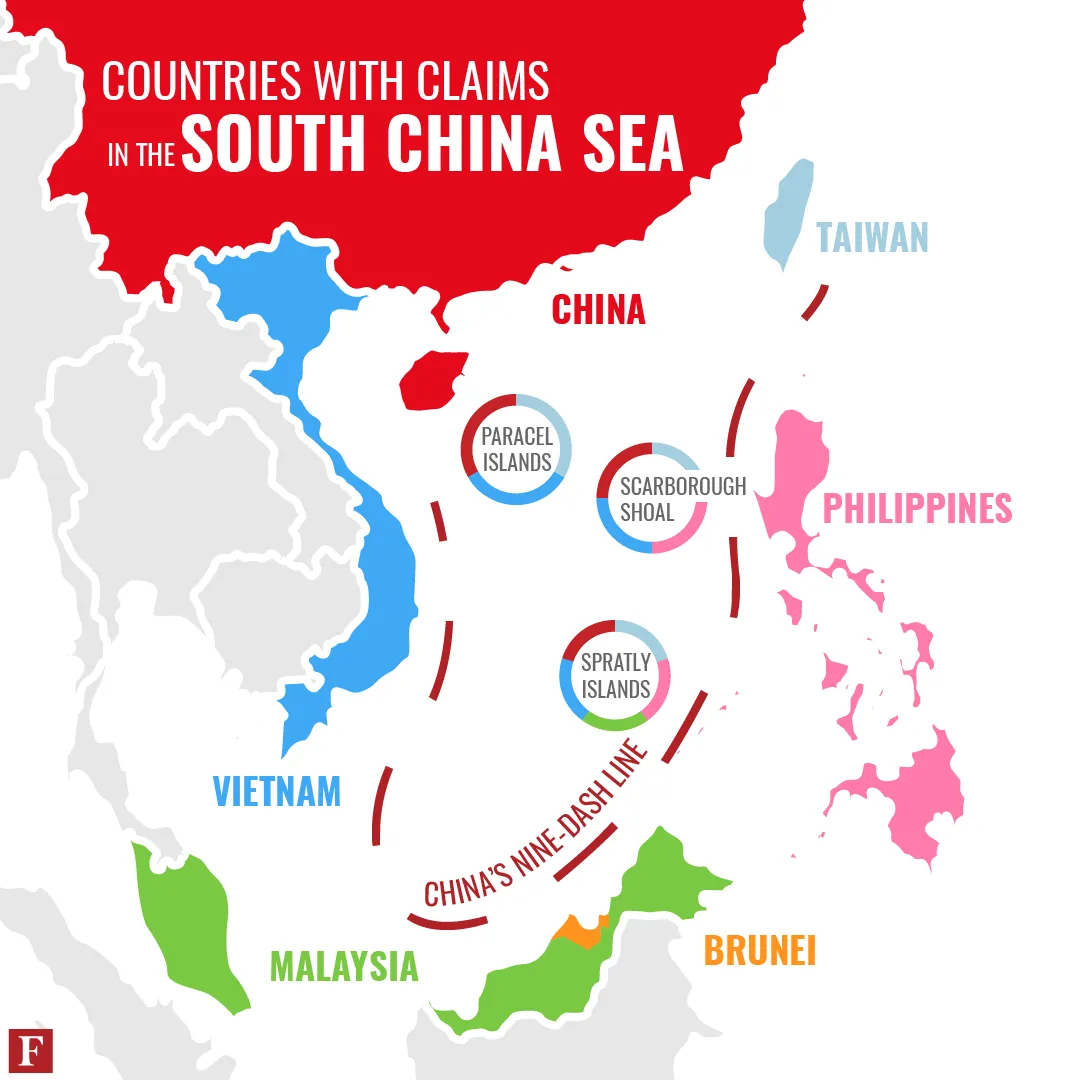
Key Features:
- China claims most of the South China Sea as its territory.
- The U.S. conducts “freedom of navigation” operations to challenge those claims.
- Regional allies like the Philippines and Vietnam are caught in the middle.
- The area is rich in resources and vital shipping routes.
- Military confrontations risk accidental escalation.
The South China Sea is another hotspot in U.S.–China relations. China has built artificial islands and military bases in disputed waters, alarming its neighbors. The U.S. regularly sends naval vessels through the area to assert international maritime rights.
These confrontations increase the chances of accidents or miscalculations. With vital shipping lanes and untapped natural resources at stake, the South China Sea dispute is about both security and economic influence. For Washington, supporting allies in the region is crucial to countering Chinese expansion.
5. Sanctions and Economic Restrictions
Key Features:
- The U.S. has imposed sanctions on Chinese companies over human rights and security concerns.
- China has responded with its own “unreliable entity list.”
- Sanctions affect global businesses tied to both economies.
- Human rights issues, especially in Xinjiang, remain a flashpoint.
- Financial restrictions are influencing global banking and investment flows.
Sanctions have become a powerful tool in the rivalry between Washington and Beijing. The U.S. has sanctioned Chinese companies for alleged involvement in human rights abuses, surveillance technologies, and military cooperation. These sanctions extend to financial institutions, limiting China’s access to global capital markets.
China has retaliated with its own measures, targeting foreign companies and creating regulatory hurdles for American firms operating in the country. The sanctions dispute highlights how economic policies are increasingly being used as weapons in the broader geopolitical struggle.
Conclusion – 5 Big Disputes Defining U.S.–China Relations This Year
The 5 big disputes defining U.S.–China relations this year – Taiwan, trade wars, AI and technology competition, South China Sea tensions, and sanctions—are reshaping the future of global politics. Each dispute is interconnected, fueling mistrust and competition between the two largest economies in the world.
While dialogue continues in some areas, the overall trajectory suggests a prolonged rivalry. The world will closely watch how these disputes unfold, as their consequences go far beyond Washington and Beijing. For now, U.S.–China relations remain one of the most critical factors influencing global peace, security, and economic growth.
Table: Overview of 5 Big Disputes Defining U.S.–China Relations
| Dispute | Key Issues | Global Impact | Current Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Taiwan | U.S. support for Taiwan vs. China’s reunification goals | Risk of military conflict, semiconductor supply chain disruption | High tension with frequent military activity |
| Trade Wars | Tariffs, subsidies, unfair practices | Inflation, supply chain shifts | Ongoing, no major resolution |
| AI & Tech Race | Semiconductors, AI dominance, 5G | Tech decoupling, global innovation split | Intensifying competition |
| South China Sea | Territorial claims, U.S. naval operations | Threat to trade routes, regional security | Ongoing disputes with rising militarization |
| Sanctions | Human rights, military ties, financial restrictions | Global business disruption | Expanding restrictions on both sides |
FAQs on 5 Big Disputes Defining U.S.–China Relations
1. Why is Taiwan the most sensitive issue in U.S.–China relations?
Because China sees it as part of its territory, while the U.S. supports Taiwan’s self-governance and security.
2. How do trade wars affect everyday consumers?
Tariffs raise the cost of goods, contributing to higher inflation and shifting supply chains.
3. What role does AI play in the U.S.–China rivalry?
AI is central to economic growth, cybersecurity, and military power, making it a strategic priority.
4. Why is the South China Sea important to both countries?
It is a vital trade route with valuable natural resources and strategic military importance.
5. What are U.S. sanctions targeting in China?
They target companies linked to human rights abuses, surveillance, and military projects.
6. How is China responding to U.S. sanctions?
By creating its own lists of “unreliable entities” and restricting foreign businesses.
7. Are U.S.–China trade tensions easing?
Not significantly—tariffs remain, and both countries are prioritizing economic independence.
8. What is the global impact of the AI race?
It could create a technological divide, forcing countries to align with either the U.S. or China.
9. Can the South China Sea dispute trigger conflict?
Yes, miscalculations or accidents between military forces could escalate quickly.
10. What is the future of U.S.–China relations?
Likely continued rivalry with selective cooperation, depending on global challenges.