Looking to rev up your metabolism? Discover the top 5 superfoods that can give your body a natural boost.
In this insightful article, we unveil the key dietary powerhouses that can kickstart your metabolism and enhance your overall well-being.
Learn about these nutrient-packed superfoods and incorporate them into your daily diet to experience a positive impact on your metabolism.
Explore the world of nutrition and discover the top 5 superfoods scientifically proven to elevate your metabolism.
Uncover the secrets behind these powerhouse foods and how they can contribute to a healthier, more energetic you.
Elevate your nutritional intake by incorporating these superfoods into your meals, and watch as your metabolism gets the boost it needs for optimal functioning.
I. Introduction
Unlock a faster metabolism with our top 5 superfoods! Burn calories like never before.
Discover the secrets to a leaner you. Boost energy and shed pounds effortlessly. Dive into a healthier, more vibrant lifestyle.
A. Brief overview of metabolism and its impact on overall health
Metabolism is the complex set of chemical reactions that occur within the cells of our body to sustain life.
It plays a vital role in converting the food we consume into energy, affecting various physiological functions. In this section, we will provide a concise overview of metabolism, emphasizing its profound impact on overall health.
Understanding the intricacies of metabolism sets the stage for appreciating the significance of maintaining a well-functioning metabolic system.
B. Introduction to the concept of superfoods and their role in boosting metabolism
As we delve into the article, it’s essential to introduce the concept of superfoods—nutrient-dense foods that offer exceptional health benefits.
These foods go beyond basic nutrition, often containing a rich array of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. In this section, we will specifically focus on how certain superfoods play a crucial role in boosting metabolism.
By exploring the science behind these foods, readers will gain insights into how incorporating them into their diet can positively impact metabolic processes.
C. Importance of incorporating nutrient-rich foods into the diet
To bridge the concepts of metabolism and superfoods, we’ll underscore the critical importance of incorporating nutrient-rich foods into one’s diet.
A well-balanced and nutrient-dense diet not only supports optimal metabolic function but also contributes to overall health and well-being.
This section serves as a foundational understanding for the subsequent exploration of specific superfoods known for their metabolism-boosting properties.
Emphasizing the link between nutrition and metabolic health encourages readers to make informed choices for a healthier lifestyle.
5. Chia seeds
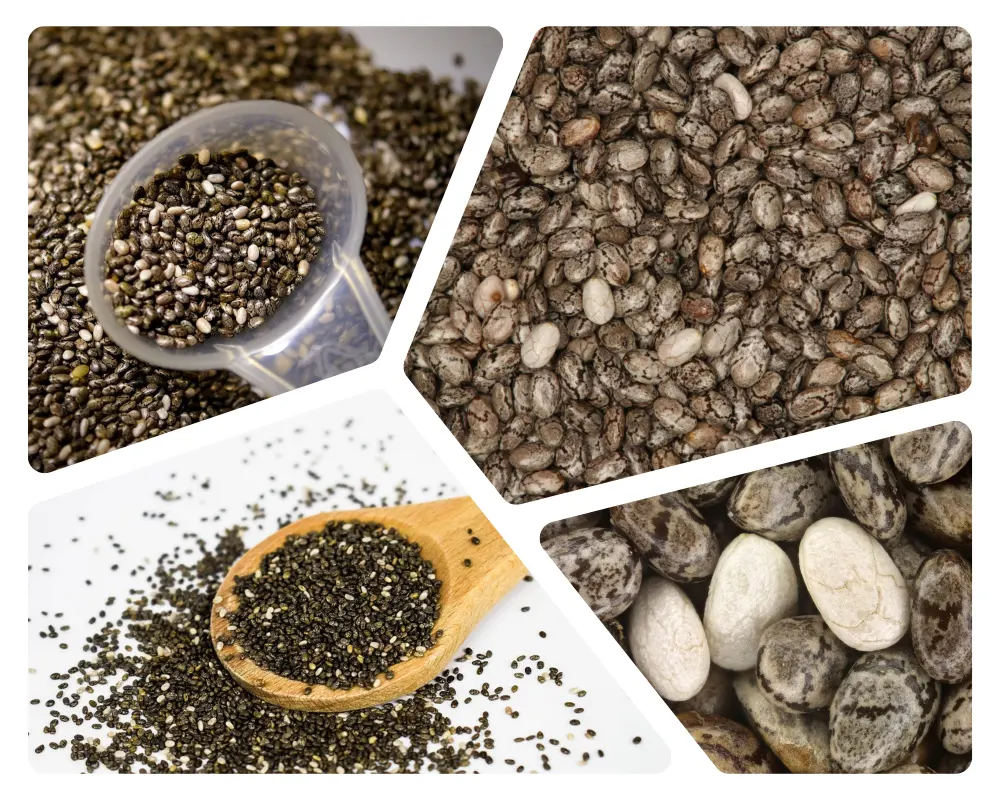

5.1 Nutritional profile and health benefits
Chia seeds have gained significant popularity in recent years due to their impressive nutritional profile and numerous health benefits.
These tiny seeds, derived from the Salvia hispanica plant, pack a powerful punch when it comes to promoting a healthy and balanced diet.
1. Nutritional profile
Fiber: Chia seeds are an excellent source of dietary fiber. Just one ounce (28 grams) of chia seeds provides around 11 grams of fiber, which is about one-third of the recommended daily intake.
This high fiber content helps promote a healthy digestive system, prevents constipation, and supports overall gut health.
Omega-3 fatty acids: Chia seeds are rich in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of omega-3 fatty acid.
These essential fats play a crucial role in reducing inflammation, supporting brain health, and promoting heart health.
Protein: Chia seeds are a good plant-based source of protein. They contain all nine essential amino acids, making them a valuable addition to a vegetarian or vegan diet. Protein is essential for muscle repair, growth, and overall cellular function.
Antioxidants: Chia seeds are packed with antioxidants, including flavonoids and phenolic compounds.
These antioxidants help protect the body against damage from harmful free radicals, thus reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
2. Health benefits
Heart health: The combination of omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and antioxidants in chia seeds contributes to heart health.
Omega-3s help lower blood pressure, reduce bad cholesterol levels, and decrease the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
The fiber content aids in maintaining healthy cholesterol levels and supports proper digestion, further benefiting heart health.
Weight management: Chia seeds can be a valuable addition to a weight management plan. The high fiber content creates a feeling of fullness, reducing appetite and preventing overeating.
Additionally, chia seeds can absorb water, forming a gel-like substance in the stomach that slows down the absorption of food and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
Energy and endurance: Chia seeds are often touted as a superfood for athletes and active individuals.
The combination of carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats in chia seeds provides a sustained release of energy, making them an ideal pre- or post-workout snack.
The hydration properties of chia seeds also help maintain electrolyte balance during exercise.
Bone health: Chia seeds are a good source of calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus, essential minerals for maintaining strong and healthy bones.
Including chia seeds in your diet can contribute to reducing the risk of osteoporosis and improving bone density.
Chia seeds are a nutrient-dense superfood that can enhance the nutritional value of your meals and contribute to a healthy and balanced diet.
Their high fiber, omega-3 fatty acid, and protein content, along with other essential nutrients, make them an excellent choice for promoting heart health, supporting digestion, and providing sustainable energy.
Consider incorporating chia seeds into your daily meals and enjoy the numerous health benefits they offer.
5.2 High fiber and protein content for sustained energy
Chia seeds have gained popularity as a superfood due to their impressive nutritional profile and numerous health benefits.
One of the key reasons chia seeds are considered a top superfood is their high fiber and protein content, which provides sustained energy and promotes overall well-being.
1. Fiber content
Chia seeds are an excellent source of dietary fiber. Just one ounce (28 grams) of chia seeds contains a remarkable 11 grams of fiber.
This high fiber content plays a crucial role in promoting digestive health and preventing constipation.
Fiber also helps regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of diabetes and providing a steady release of energy throughout the day.
Additionally, chia seeds’ fiber content aids in weight management by promoting a feeling of fullness and reducing overall calorie intake.
2. Protein content
Chia seeds are an exceptional plant-based source of protein.
They contain all nine essential amino acids, making them a complete protein source. In just one ounce of chia seeds, you’ll find around 4 grams of protein.
Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, supporting muscle growth, and maintaining a healthy immune system.
Including chia seeds in your diet can be especially beneficial for individuals following a vegetarian or vegan lifestyle, as they provide a valuable plant-based protein source.
3. Sustained energy
The combination of high fiber and protein content in chia seeds contributes to sustained energy levels.
The fiber slows down the digestion process, allowing for a gradual release of carbohydrates into the bloodstream.
This steady release of energy prevents blood sugar spikes and crashes, promoting stable energy levels throughout the day.
The protein content in chia seeds also helps in energy production, as proteins are broken down into amino acids that the body uses for various functions, including energy production.
4. Other health benefits
In addition to their fiber and protein content, chia seeds offer several other health benefits.
They are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for brain health, reducing inflammation, and supporting heart health.
Chia seeds are also packed with antioxidants, which help protect the body against free radicals and oxidative stress.
Furthermore, they contain essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus, which are vital for bone health.
Incorporating Chia Seeds Into Your Diet
To enjoy the benefits of chia seeds, there are several ways you can incorporate them into your diet:
1. Chia seed pudding: Mix chia seeds with your choice of milk, sweetener, and flavorings to create a delicious and nutritious pudding.
2. Smoothies: Add a tablespoon or two of chia seeds to your favorite smoothie recipe for an extra boost of fiber and protein.
3. Baking: Use chia seeds as an egg substitute in baking recipes by mixing them with water to form a gel-like consistency.
4. Toppings: Sprinkle chia seeds on top of yogurt, oatmeal, or salads to add a crunchy texture and a nutrient boost.
Chia seeds are a true superfood, offering high fiber and protein content for sustained energy and overall well-being.
Incorporating chia seeds into your daily meals can help support digestive health, provide essential nutrients, and contribute to a balanced and healthy diet.
So go ahead and start reaping the benefits of chia seeds by including them in your favorite recipes and enjoying their nutritional goodness.
5.3 Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Their Impact on Heart Health
Chia seeds have gained significant popularity in recent years due to their impressive nutritional profile and numerous health benefits.
One of the key reasons chia seeds are considered a superfood is their high content of omega-3 fatty acids, which play a crucial role in supporting heart health.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Heart Health
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fat that has been extensively studied for its positive effects on cardiovascular health.
These essential fats cannot be produced by the body, so they must be obtained through diet.
Chia seeds are an excellent plant-based source of omega-3 fatty acids, specifically alpha-linolenic acid (ALA).
- Lowering Risk Factors
Consuming chia seeds regularly can help lower several risk factors associated with heart disease.
Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to reduce blood pressure, triglyceride levels, and LDL cholesterol (often referred to as “bad” cholesterol).
By promoting healthier lipid profiles, chia seeds contribute to a decreased risk of developing heart disease.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties
Inflammation is a common factor in the development of cardiovascular diseases.
Omega-3 fatty acids found in chia seeds possess anti-inflammatory properties, helping to reduce inflammation in the body.
By reducing inflammation, chia seeds can support heart health and lower the risk of developing chronic conditions such as atherosclerosis.
- Blood Clot Prevention
Another benefit of omega-3 fatty acids is their ability to prevent the formation of blood clots.
Blood clots can lead to serious complications, such as heart attacks and strokes.
Chia seeds’ omega-3 content helps maintain the flexibility of blood vessels, preventing clot formation and improving blood flow.
- Improving Heart Rhythm
Omega-3 fatty acids also contribute to maintaining a healthy heart rhythm.
They help regulate electrical signaling in the heart, reducing the risk of arrhythmias and promoting a steady heartbeat.
This is particularly beneficial for individuals with preexisting heart conditions or those at risk of irregular heart rhythms.
- Incorporating Chia Seeds Into the Diet
Chia seeds can be easily incorporated into the diet by adding them to smoothies, yogurt, oatmeal, or baked goods.
They have a mild, nutty flavor and a unique gel-like texture when soaked in liquid, making them versatile and enjoyable to include in various recipes.
Chia seeds are a superfood known for their rich omega-3 fatty acid content, which has a profound impact on heart health.
Including chia seeds in your diet can help lower risk factors associated with heart disease, reduce inflammation, prevent blood clot formation, and support a healthy heart rhythm.
By incorporating these tiny seeds into your daily meals, you can take a significant step toward maintaining a healthy and balanced cardiovascular system.
4. Salmon
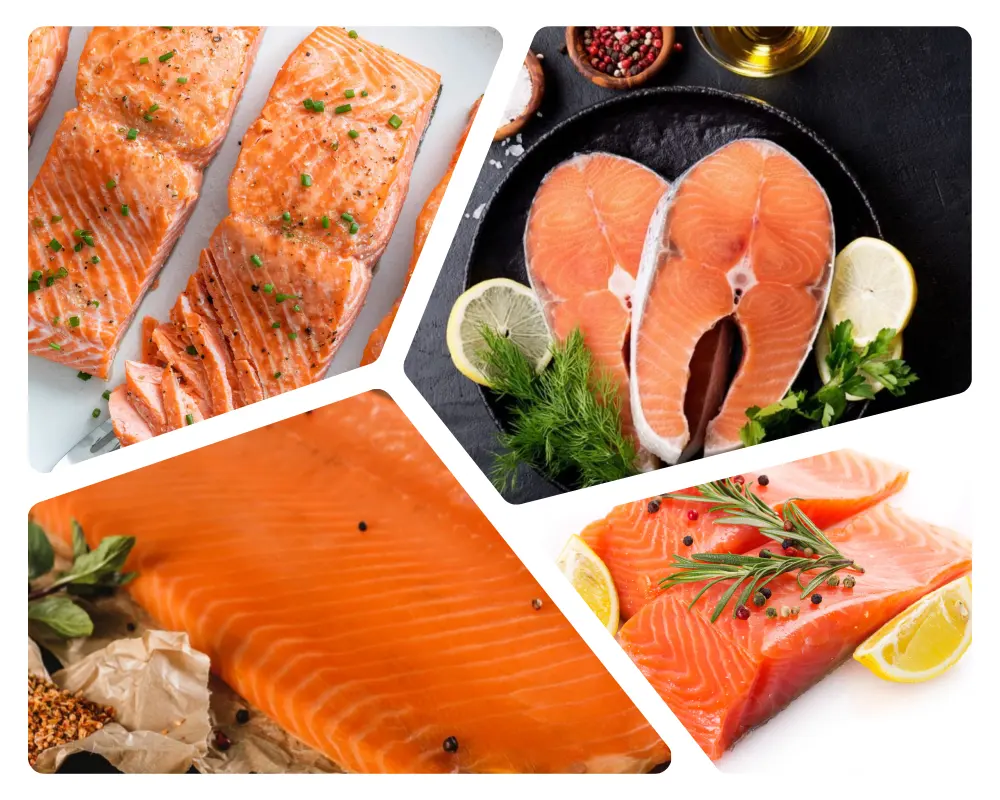

4.1 Nutritional profile and health benefits
Salmon is often regarded as one of the healthiest foods available due to its exceptional nutritional content and numerous health benefits.
Here, we will explore its nutritional profile and delve into the specific advantages it offers to a healthy and balanced diet.
1. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Salmon is particularly renowned for its high concentration of omega-3 fatty acids, specifically eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
These essential fatty acids play a crucial role in supporting brain health, reducing inflammation, and promoting cardiovascular well-being.
EPA and DHA are associated with a decreased risk of heart disease, lower blood pressure levels, and improved cognitive function.
2. Protein: Salmon is an excellent source of high-quality protein.
A 3-ounce serving of salmon provides about 22 grams of protein, making it a valuable option for individuals looking to build and maintain muscle mass.
Protein is vital for tissue repair, enzymatic functions, hormone production, and overall growth and development.
3. Vitamin D: Salmon is one of the best dietary sources of vitamin D, a nutrient crucial for bone health, immune function, and overall well-being.
Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium and promotes its incorporation into bones, thus preventing conditions like osteoporosis.
Adequate vitamin D intake also plays a role in supporting a healthy immune system.
4. B Vitamins: Salmon is rich in various B vitamins, including vitamin B12, niacin (B3), pyridoxine (B6), and riboflavin (B2).
These vitamins are essential for energy production, brain function, red blood cell formation, and nerve health.
Vitamin B12, in particular, is primarily found in animal-based foods like salmon and is crucial for maintaining a healthy nervous system.
5. Minerals: Salmon contains an array of minerals that contribute to overall health. These include potassium, selenium, and phosphorus.
Potassium is essential for maintaining proper heart and muscle function, while selenium acts as a powerful antioxidant, supporting the immune system and protecting against oxidative damage.
Phosphorus plays a vital role in bone health, energy production, and DNA synthesis.
6. Astaxanthin: Astaxanthin is a powerful antioxidant found in salmon, responsible for its distinctive pink color.
This antioxidant has been associated with various health benefits, including reducing inflammation, improving skin health, and supporting eye health.
4.2 Omega-3 fatty acids and their positive effects on brain health
Salmon, a delicious and nutritious fish, is renowned for its high content of omega-3 fatty acids.
These essential fatty acids play a vital role in promoting optimal brain health and function. Let’s explore in detail the positive effects of omega-3 fatty acids found in salmon on the brain.
- Cognitive Function
Omega-3 fatty acids are crucial for the development and maintenance of brain cells.
They help support healthy brain structure and function, particularly in areas associated with memory, learning, and cognitive performance.
Studies have shown that individuals with higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids in their diet tend to have better cognitive abilities and a reduced risk of cognitive decline, including conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and dementia.
- Mood and Mental Health
The omega-3 fatty acids found in salmon are involved in the synthesis and regulation of neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers in the brain that influence mood and emotions.
Adequate levels of omega-3s have been associated with a lower risk of depression and anxiety disorders.
Additionally, research suggests that omega-3 supplementation may be beneficial in reducing symptoms of depression and improving overall mood.
- Brain Development
Omega-3 fatty acids, specifically docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), are crucial for brain development in infants and young children.
DHA makes up a significant portion of the brain’s structural fats, especially during the early stages of life.
Pregnant women who consume omega-3-rich foods like salmon may support their baby’s brain development, leading to improved cognitive abilities and better visual function.
- Neuroprotective Properties
Omega-3 fatty acids exhibit neuroprotective properties, which means they help safeguard the brain against damage and promote its resilience.
They have been found to reduce inflammation in the brain, protect against oxidative stress, and enhance blood flow and oxygen delivery to brain cells.
These effects contribute to a healthier brain and may help reduce the risk of neurological disorders, such as stroke and age-related cognitive decline.
- Eye Health
Apart from their brain-boosting benefits, omega-3 fatty acids found in salmon also play a role in maintaining good eye health.
DHA, one of the key omega-3s, is a major component of the retina.
Adequate intake of omega-3s has been associated with a reduced risk of age-related macular degeneration and dry eye syndrome, two common eye conditions that can affect vision.
Incorporating salmon into your diet at least twice a week can provide you with a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids. Grilling, baking, or steaming salmon are healthy cooking methods that help preserve its nutritional value.
However, it’s important to consider the source of salmon and opt for wild-caught or sustainably farmed varieties to minimize exposure to contaminants and ensure the highest quality fish.
Salmon’s omega-3 fatty acids offer a range of benefits for brain health.
From supporting cognitive function and mood to promoting brain development and protecting against neurological disorders, incorporating this superfood into your diet can have a positive impact on your overall brain health and well-being.
4.3 Protein Source with Essential Amino Acids
Salmon, often referred to as the “king of fish,” is not only a delicious addition to any meal but also a nutrient powerhouse.
This superfood is an excellent source of high-quality protein, providing essential amino acids that are vital for various functions in the body.
1. Nutritional Profile and Health Benefits
– Salmon is rich in vitamins and minerals, including vitamin D, vitamin B12, selenium, and potassium, which contribute to overall health and well-being.
– It is a great source of lean protein, with a 3.5-ounce serving containing about 22 grams of protein.
– Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, supporting the immune system, and producing enzymes and hormones.
2. Essential Amino Acids
– Salmon is a complete protein source, meaning it contains all the essential amino acids required by the body.
– Essential amino acids cannot be produced by the body and must be obtained through the diet.
– These amino acids play a crucial role in muscle synthesis, promoting muscle growth and repair.
– They are also involved in various physiological processes, such as neurotransmitter synthesis, hormone regulation, and immune function.
3. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Brain Health
– In addition to being a valuable protein source, salmon is renowned for its high content of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid).
– Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that have been linked to numerous health benefits, including improved brain health.
– DHA, in particular, is a major structural component of the brain and supports cognitive function, memory, and overall brain health.
– Consuming salmon regularly can help enhance brain development in children and potentially reduce the risk of age-related cognitive decline in adults.
4. Heart Health Benefits
– The omega-3 fatty acids found in salmon have been extensively studied for their positive impact on heart health.
– They can help lower triglyceride levels, reduce inflammation, improve blood flow, and decrease the risk of cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attacks and strokes.
– The protein content in salmon also contributes to heart health by assisting in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
Incorporating salmon into your diet provides an array of health benefits, thanks to its protein content and essential amino acids.
Whether grilled, baked, or poached, this versatile superfood can be enjoyed in various dishes.
Remember to choose wild-caught salmon whenever possible, as it tends to have a higher omega-3 fatty acid content.
By including salmon in your meals, you can support muscle growth, brain function, and heart health while enjoying a delicious and nutritious food option.
3. Quinoa
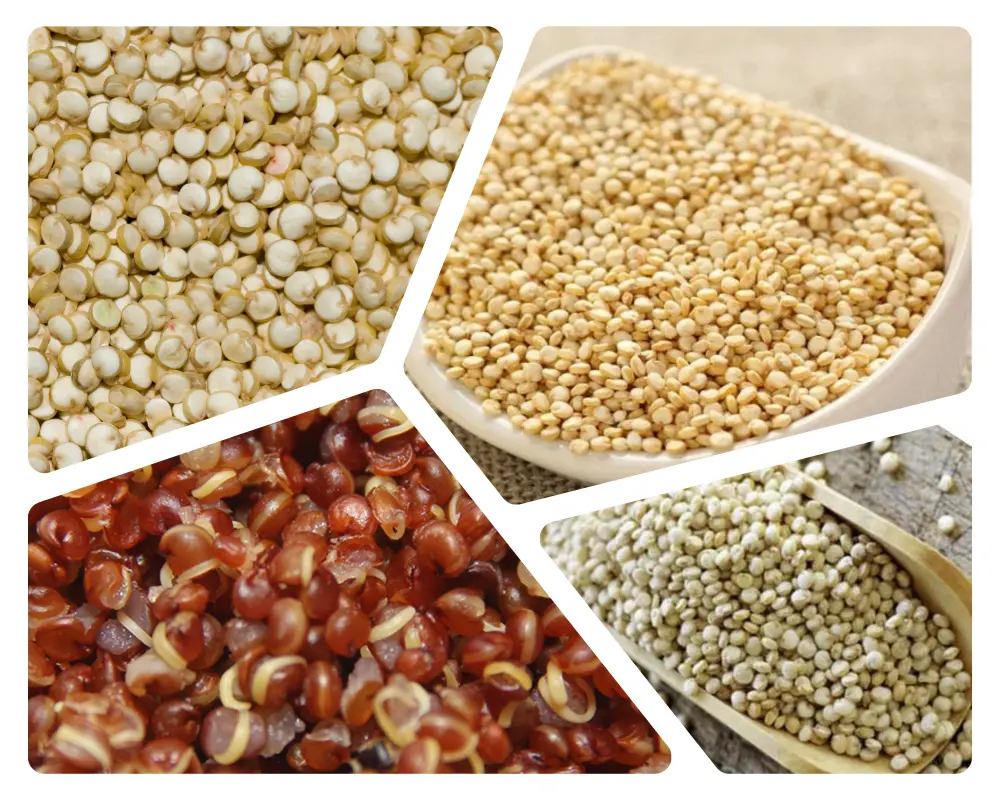

3.1 Nutritional profile and health benefits
Quinoa (pronounced keen-wah) is a highly nutritious pseudo-cereal that has gained significant popularity in recent years due to its numerous health benefits.
Here, we delve into its impressive nutritional profile and explore the various ways it contributes to a healthy and balanced diet.
1. Rich in essential nutrients
Quinoa is a powerhouse of essential nutrients that are vital for overall health and well-being.
It is a great source of high-quality protein, containing all nine essential amino acids, making it an excellent choice for vegans and vegetarians.
It is also rich in complex carbohydrates, dietary fiber, and a range of vitamins and minerals, including magnesium, iron, potassium, and B-vitamins.
2. Gluten-free and suitable for various dietary needs
One of the remarkable qualities of quinoa is that it is naturally gluten-free, making it a suitable grain alternative for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivities.
Its versatility also makes it an excellent choice for those following specific dietary patterns, such as vegan, vegetarian, or plant-based diets.
3. Supports heart health
Quinoa is a heart-healthy food due to its unique composition. It is a good source of dietary fiber, which can help reduce cholesterol levels and lower the risk of heart disease.
Quinoa also contains heart-healthy fats, such as omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties and can contribute to cardiovascular health.
4. Promotes digestion and weight management
The high fiber content in quinoa plays a crucial role in promoting healthy digestion. Fiber adds bulk to the stool, facilitating regular bowel movements and preventing constipation.
Additionally, the fiber in quinoa helps promote satiety, keeping you feeling fuller for longer periods, which can aid in weight management and prevent overeating.
5. Supports blood sugar control
Quinoa has a low glycemic index, which means it doesn’t cause significant spikes in blood sugar levels after consumption.
This makes it a favorable choice for individuals with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar levels.
The combination of fiber, protein, and healthy fats in quinoa helps slow down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, leading to a more gradual release of glucose into the bloodstream.
6. Provides antioxidant protection
Quinoa contains various antioxidants, including flavonoids and polyphenols, which help protect the body against oxidative stress caused by harmful free radicals.
These antioxidants have been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders.
3.2 High protein content and role in muscle repair and growth
Quinoa, often referred to as a “pseudo-grain,” is a superfood that stands out for its exceptional protein content.
Unlike other grains, quinoa is a complete protein source, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own.
This makes it an excellent addition to a balanced diet, especially for individuals following a vegetarian or vegan lifestyle.
- Nutritional profile
– Quinoa is packed with nutrients that promote overall health and well-being. It is rich in essential minerals such as iron, magnesium, and phosphorus, which are crucial for various bodily functions.
– A 1-cup serving of cooked quinoa provides approximately 8 grams of protein, making it an ideal option for those looking to increase their protein intake.
- Muscle repair and growth
– Protein plays a vital role in muscle repair and growth, making quinoa an excellent choice for athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and individuals recovering from injuries.
– The amino acids found in quinoa, particularly lysine and isoleucine, are important for muscle synthesis and repair. Lysine, in particular, aids in the formation of collagen, a protein that provides structure and strength to muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
– Quinoa’s protein content helps replenish the amino acid pool in the body, ensuring proper muscle recovery and reducing the risk of muscle breakdown.
- Supporting exercise performance
– Quinoa’s high protein content provides a sustained release of energy, making it an ideal food to fuel workouts and physical activities.
– Additionally, quinoa contains complex carbohydrates that contribute to glycogen storage in muscles. This helps maintain energy levels during exercise and supports endurance and performance.
- Versatility in recipes
– Quinoa is incredibly versatile and can be incorporated into various meals. It can serve as a base for salads, stir-fries, or grain bowls, or be used as a substitute for rice or pasta.
– It can also be ground into flour and used for baking, adding a nutritious boost to bread, muffins, and other baked goods.
3.3 Rich in Fiber and Its Impact on Heart Health
Quinoa, often hailed as a superfood, is not only delicious and versatile but also offers numerous health benefits, particularly in relation to heart health. One of the key factors that contribute to its heart-healthy properties is its high fiber content.
1. Fiber and Heart Health
a. Cholesterol Management: Quinoa contains both soluble and insoluble fiber.
Soluble fiber acts as a cholesterol-lowering agent by binding to cholesterol in the digestive system and preventing its absorption into the bloodstream.
By reducing LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, soluble fiber helps lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes.
b. Blood Pressure Regulation: The fiber content in quinoa also plays a role in regulating blood pressure.
Soluble fiber aids in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels by reducing the absorption of sodium and promoting the excretion of excess water from the body. This helps to prevent hypertension and its associated risks.
2. Nutritional Profile of Quinoa
a. Fiber Content: Quinoa is considered an excellent source of dietary fiber.
In just one cup of cooked quinoa, you can obtain approximately 5 grams of fiber, which contributes to the recommended daily intake of fiber for adults.
Adequate fiber intake is essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system and promoting overall well-being.
b. Other Nutrients: Along with its fiber content, quinoa is rich in various other nutrients that support heart health, such as magnesium and potassium.
Magnesium helps regulate blood pressure, while potassium helps maintain heart rhythm and supports optimal cardiovascular function.
3. Incorporating Quinoa into a Heart-Healthy Diet
a. Replace Refined Grains: Quinoa can be an excellent substitute for refined grains like white rice or pasta.
Its nutty flavor and unique texture make it a satisfying addition to salads, stir-fries, and even as a base for grain bowls.
By swapping refined grains with quinoa, you can increase your fiber intake and promote heart health.
b. Balanced Meals: Incorporate quinoa into balanced meals by combining it with lean proteins, such as grilled chicken or tofu, and a variety of colorful vegetables.
This ensures you get a diverse range of nutrients along with the fiber content provided by quinoa.
4. Other Benefits of Quinoa
a. Nutrient Density: Quinoa is a nutrient-dense food, meaning it provides a substantial amount of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants in relation to its calorie content.
These nutrients play a vital role in supporting overall health and well-being.
b. Satiety and Weight Management: The high fiber and protein content in quinoa can promote feelings of fullness and help manage weight.
By incorporating quinoa into your meals, you may experience increased satiety, making it easier to control portion sizes and maintain a healthy weight.
Quinoa’s rich fiber content makes it an excellent addition to a heart-healthy diet. Its ability to manage cholesterol levels, regulate blood pressure, and provide various other essential nutrients contributes to its reputation as a superfood.
By incorporating quinoa into your meals, you can enjoy its delicious taste while promoting optimal heart health and overall well-being.
2. Kale
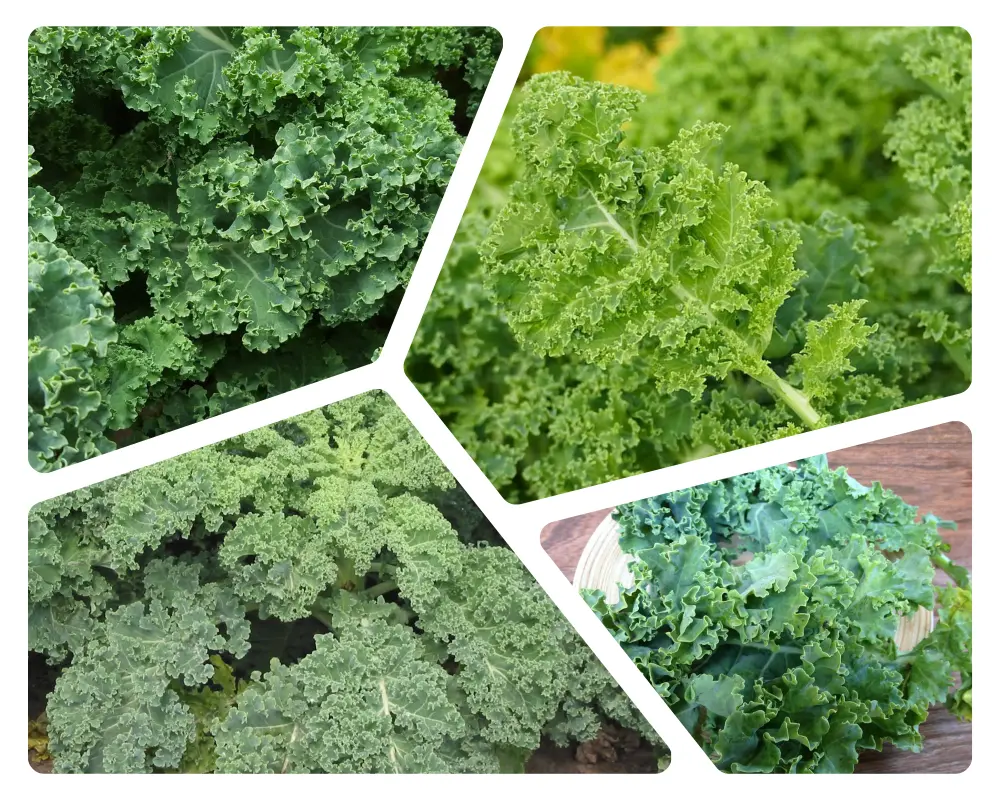

2.1 Nutritional profile and health benefits
Kale is often hailed as a nutritional powerhouse due to its impressive nutrient profile. Here are some key nutrients found in kale and their associated health benefits:
1. Vitamins: Kale is rich in various vitamins, particularly vitamins A, C, and K. Vitamin A is essential for maintaining healthy vision, promoting immune function, and supporting cell growth and development.
Vitamin C is an antioxidant that helps boost the immune system, aids in collagen production, and protects cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Vitamin K plays a vital role in blood clotting, bone health, and cardiovascular health.
2. Minerals: Kale is an excellent source of minerals such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium.
Potassium helps regulate blood pressure, supports proper muscle and nerve function, and assists in maintaining a healthy balance of fluids in the body.
Calcium is crucial for building and maintaining strong bones and teeth, as well as ensuring proper muscle function.
Magnesium is involved in more than 300 biochemical reactions in the body and contributes to energy production, nerve function, and muscle relaxation.
3. Antioxidants: Kale contains various antioxidants, including beta-carotene, flavonoids, and quercetin.
These antioxidants help combat oxidative stress and reduce inflammation in the body, potentially lowering the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and certain types of cancer.
They also play a role in promoting skin health and preventing premature aging.
4. Fiber: Kale is an excellent source of dietary fiber, both soluble and insoluble.
Fiber aids in digestion, promotes regular bowel movements, and helps maintain healthy cholesterol and blood sugar levels.
Additionally, it contributes to a feeling of fullness, making it beneficial for weight management.
5. Phytochemicals: Kale contains a variety of phytochemicals, including sulforaphane and indole-3-carbinol, which have been associated with potential anticancer effects.
These compounds help support the body’s natural detoxification processes and may help protect against certain types of cancer, such as colon, breast, and prostate cancer.
2.2 Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants
Kale is a leafy green vegetable that has gained tremendous popularity in recent years due to its exceptional nutritional content.
It is often referred to as a superfood because it is packed with a wide array of essential vitamins, minerals, and powerful antioxidants, all of which contribute to its numerous health benefits.
- Vitamins
– Vitamin A: Kale is an excellent source of vitamin A, which is vital for maintaining healthy vision, supporting the immune system, and promoting cell growth and development.
– Vitamin C: Kale is incredibly rich in vitamin C, an antioxidant that plays a crucial role in boosting the immune system, promoting collagen synthesis for healthy skin, and protecting cells from damage caused by harmful free radicals.
– Vitamin K: Kale is one of the best dietary sources of vitamin K, which is essential for blood clotting, bone health, and may even help reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
– B-vitamins: Kale contains several B-vitamins, including folate (essential for cell growth and development), vitamin B6 (important for brain health and metabolism), and riboflavin (involved in energy production and red blood cell formation).
- Minerals
– Calcium: Kale is a remarkable source of calcium, which is essential for maintaining strong bones and teeth, regulating muscle function, and supporting nerve transmission.
– Potassium: Kale is rich in potassium, a mineral that helps maintain healthy blood pressure, supports proper muscle and nerve function, and aids in fluid balance within the body.
– Magnesium: Kale contains a good amount of magnesium, which is involved in more than 300 enzymatic reactions in the body, including energy production, protein synthesis, and nerve function.
- Antioxidants
– Carotenoids: Kale contains carotenoids such as beta-carotene, lutein, and zeaxanthin, which have potent antioxidant properties.
These compounds help protect the body against oxidative stress, reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and certain types of cancer.
– Flavonoids: Kale is also rich in flavonoids, including quercetin and kaempferol, which have anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties.
These compounds may help lower the risk of chronic diseases and support overall health.
Incorporating kale into your diet is relatively easy. It can be enjoyed raw in salads, sautéed as a side dish, or blended into smoothies. Its versatility allows for creative culinary uses, making it a versatile and nutritious addition to any meal.
By including kale in your diet, you can reap the numerous health benefits associated with its abundance of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
From supporting immune function to promoting bone health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases, kale is a true powerhouse vegetable that can contribute to a healthy and balanced diet.
2.3 Potential Anti-Cancer Properties
Kale, a leafy green vegetable from the cabbage family, has gained significant attention for its potential anti-cancer properties.
This nutrient-dense superfood contains a variety of compounds that have been studied for their ability to inhibit the growth of cancer cells and reduce the risk of developing certain types of cancer.
Here are some details on kale’s potential anti-cancer properties:
1. Phytochemicals
Kale is rich in phytochemicals, which are natural compounds found in plants that have been associated with cancer prevention.
One such group of phytochemicals found in kale is glucosinolates. When broken down during digestion or food preparation, glucosinolates are converted into biologically active compounds, such as indole-3-carbinol (I3C) and sulforaphane.
These compounds have shown promising effects in studies on cancer prevention and treatment.
2. Antioxidant Effects
Kale contains high levels of antioxidants, including beta-carotene, vitamin C, and various flavonoids.
These antioxidants help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, which can damage DNA and potentially lead to the development of cancer.
By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, kale’s antioxidant content may help protect against cancer formation.
3. Anti-inflammatory Properties
Chronic inflammation is associated with an increased risk of cancer.
Kale contains compounds, such as kaempferol and quercetin, which have demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects.
These compounds help reduce inflammation in the body, potentially lowering the risk of cancer development.
4. Detoxification Support
Kale contains nutrients that support the body’s natural detoxification processes.
The liver plays a crucial role in eliminating toxins from the body, including harmful substances that may contribute to cancer development.
Certain compounds in kale, such as sulfur-containing phytochemicals, assist the liver in breaking down and removing carcinogens, thus supporting overall detoxification and potentially reducing cancer risk.
5. Fiber Content
Kale is an excellent source of dietary fiber. Adequate fiber intake is associated with a reduced risk of colorectal cancer.
Fiber helps promote regular bowel movements, prevents constipation, and aids in the elimination of waste and toxins from the body.
By maintaining a healthy digestive system, kale’s fiber content may contribute to a lower risk of cancer in the digestive tract.
It’s important to note that while kale shows promise in terms of its potential anti-cancer properties, no single food can guarantee the prevention or treatment of cancer. A healthy and balanced diet, along with other lifestyle factors, plays a crucial role in overall cancer prevention.
Incorporating kale into a varied and nutrient-rich diet, along with regular physical activity, avoiding tobacco, and maintaining a healthy weight, can contribute to reducing the risk of cancer and promoting overall well-being.
Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance on diet, lifestyle, and cancer prevention strategies.
1. Blueberries
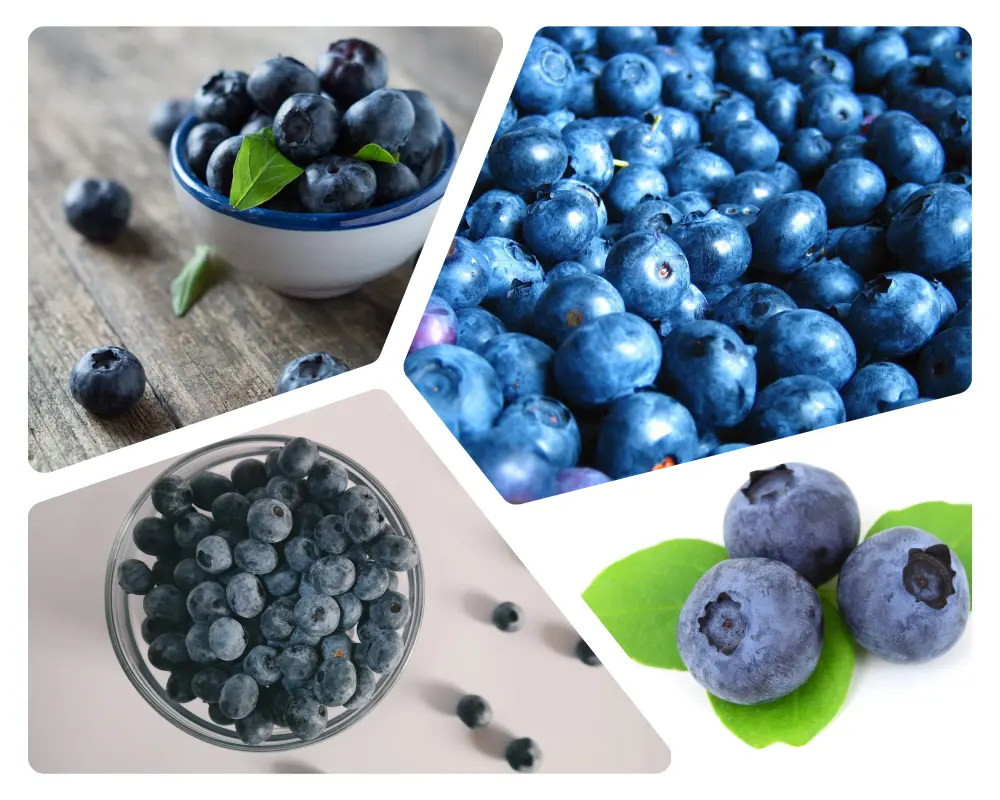

1.1 Nutritional profile and health benefits
Blueberries are small, vibrant berries that are not only delicious but also packed with essential nutrients. Here, we will delve into their nutritional profile and explore the numerous health benefits they offer.
- Antioxidant Powerhouse
Blueberries are known for their exceptional antioxidant content, particularly anthocyanins.
These compounds give blueberries their deep blue color and play a vital role in protecting the body against oxidative stress caused by harmful free radicals.
By neutralizing these free radicals, blueberries help reduce the risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
- Rich in Vitamins and Minerals
Blueberries are a fantastic source of several essential vitamins and minerals that support overall health.
They are notably high in vitamin C, which strengthens the immune system and aids in collagen synthesis.
Additionally, blueberries provide vitamin K for blood clotting, manganese for bone health and metabolism, and potassium for maintaining healthy blood pressure.
- Fiber Content for Digestive Health
Blueberries are an excellent source of dietary fiber, promoting a healthy digestive system.
Fiber aids in regular bowel movements, prevents constipation, and supports gut health by promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
Furthermore, the fiber in blueberries can help regulate blood sugar levels, making them a suitable option for individuals with diabetes or those aiming to manage their blood glucose levels.
- Cardiovascular Benefits
Consuming blueberries regularly can contribute to heart health due to their potential cardiovascular benefits.
The antioxidants in blueberries help reduce oxidative stress, which can lead to the development of heart disease.
Blueberries have been associated with lowering blood pressure, reducing LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, and improving overall blood vessel function, all of which contribute to a healthier cardiovascular system.
- Brain Boosting
Blueberries are often referred to as “brain food” due to their potential cognitive benefits.
The antioxidants in blueberries have been linked to improved brain function, including enhanced memory and learning capabilities.
Studies suggest that regular blueberry consumption may help delay age-related cognitive decline and improve overall brain health.
Incorporating blueberries into your diet
To reap the benefits of blueberries, consider adding them to your meals and snacks. Enjoy them as a topping for yogurt or oatmeal, blend them into smoothies, or simply enjoy a handful as a nutritious snack.
Frozen blueberries are also a convenient option when fresh berries are out of season. Aim to include blueberries as part of a well-rounded, balanced diet for optimal health and wellness.
Remember, while superfoods like blueberries offer numerous health benefits, they should be consumed as part of an overall varied and balanced diet that includes a wide range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
1.2 Antioxidant Properties and Role in Fighting Inflammation
Blueberries are often hailed as one of the most powerful superfoods due to their impressive antioxidant properties and their ability to combat inflammation in the body.
In this section, we will delve deeper into the specific antioxidant compounds found in blueberries and their role in promoting health and well-being.
1. Anthocyanins: Blueberries owe their vibrant blue color to a group of antioxidants called anthocyanins.
These compounds have been shown to possess powerful anti-inflammatory properties.
They help to neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, which are unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to chronic inflammation.
2. Flavonoids: Blueberries are rich in flavonoids, a diverse class of antioxidants known for their anti-inflammatory effects.
Quercetin and kaempferol are two flavonoids commonly found in blueberries.
They have been linked to reduced inflammation by inhibiting certain inflammatory enzymes and signaling pathways in the body.
3. Vitamin C: Blueberries are an excellent source of vitamin C, a potent antioxidant that plays a crucial role in protecting cells from oxidative stress.
Vitamin C also supports the immune system and helps to strengthen blood vessels and collagen, promoting overall skin health.
4. Resveratrol: Resveratrol, another powerful antioxidant found in blueberries, has garnered attention for its potential anti-inflammatory effects.
It has been shown to inhibit the production of inflammatory molecules and modulate immune responses, contributing to a reduced risk of chronic diseases.
5. Anti-Inflammatory Effects: The combined action of these antioxidants in blueberries helps to combat inflammation throughout the body.
Chronic inflammation is associated with various health conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and certain cancers.
Regular consumption of blueberries can help lower the levels of inflammation markers and mitigate the risk of these conditions.
6. Brain Health: Blueberries have also been extensively studied for their potential benefits to brain health.
The antioxidants in blueberries have been found to cross the blood-brain barrier and accumulate in areas of the brain responsible for memory and learning.
This has led to promising research indicating that blueberries may improve brain function and delay age-related cognitive decline.
7. Incorporating Blueberries into the Diet: To enjoy the anti-inflammatory benefits of blueberries, it is recommended to include them in your diet on a regular basis.
Fresh or frozen blueberries can be added to smoothies, cereals, yogurt, or enjoyed as a standalone snack.
Including a variety of berries in your diet can provide a broader range of health benefits.
1.3 High fiber content and impact on digestion
Blueberries are not only delicious but also packed with essential nutrients that promote good health.
One notable aspect of blueberries is their high fiber content, which plays a significant role in supporting a healthy digestive system.
In this section, we will delve into the details of how blueberries’ fiber content positively impacts digestion.
- Fiber content of blueberries
Blueberries are an excellent source of dietary fiber. A one-cup serving of blueberries contains about 4 grams of fiber, which is approximately 14% of the recommended daily intake for an adult.
This soluble and insoluble fiber combination is beneficial for digestive health.
- Promoting regular bowel movements
The soluble fiber in blueberries absorbs water in the digestive tract, forming a gel-like substance.
This helps add bulk to the stool and promotes regular bowel movements, preventing constipation.
Consuming an adequate amount of fiber from foods like blueberries can contribute to maintaining a healthy digestive system and preventing digestive issues.
- Supporting gut health
Blueberries contain a type of fiber called prebiotics, which acts as food for the beneficial bacteria in the gut.
These bacteria, known as probiotics, play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy balance in the gut microbiome.
By nourishing the probiotics, the prebiotic fiber in blueberries helps support the growth and activity of these beneficial bacteria, promoting a healthy gut environment.
- Enhancing nutrient absorption
Fiber plays a role in slowing down the digestion process, allowing for better nutrient absorption in the small intestine.
By promoting a slower release of sugars, fiber can help stabilize blood sugar levels and prevent rapid spikes.
Additionally, the presence of fiber in the digestive system can bind to cholesterol and aid in its elimination, supporting heart health.
- Providing satiety and weight management
High-fiber foods like blueberries can help you feel fuller for longer periods, reducing the likelihood of overeating and supporting weight management efforts.
The fiber content in blueberries adds bulk to your meals, increasing satiety without adding excessive calories.
Incorporating blueberries into your diet is a simple and tasty way to boost your fiber intake and support a healthy digestive system. Consider adding them to your breakfast cereal, blending them into smoothies, or enjoying them as a standalone snack.
Remember to combine blueberries with a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of other fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins for overall health and well-being.
II. Tips for Maximizing Metabolism with Superfoods
Unlock the full potential of your metabolism by strategically combining superfoods for synergistic effects, practicing portion control and mindful eating, and complementing your superfood-rich diet with regular physical activity.
These tips offer a comprehensive approach to maximizing metabolic health and overall well-being.
A. Combining superfoods for synergistic effects
Unlock the full potential of superfoods by strategically combining them to achieve synergistic effects.
Certain combinations can enhance nutrient absorption and overall effectiveness.
This section will explore synergies between different superfoods, providing readers with practical tips on how to optimize their metabolic benefits through thoughtful dietary pairings.
Understanding the science behind these combinations empowers individuals to make informed choices when incorporating superfoods into their daily meals.
B. Portion control and mindful eating for metabolic health
In the pursuit of a boosted metabolism, it’s crucial to highlight the role of portion control and mindful eating.
This section will delve into the connection between portion sizes, metabolic efficiency, and overall health.
By adopting mindful eating habits, individuals can better regulate their calorie intake, support weight management, and promote a more balanced metabolism.
Practical tips and insights will guide readers on how to cultivate mindful eating practices for sustained metabolic health.
C. Regular physical activity to complement a superfood-rich diet
A holistic approach to maximizing metabolism involves integrating regular physical activity with a superfood-rich diet.
In this section, we will emphasize the symbiotic relationship between exercise and metabolic function.
Readers will gain insights into the types of exercises that can specifically enhance the metabolic benefits of superfoods.
By understanding how physical activity complements dietary choices, individuals can create a comprehensive lifestyle strategy for optimizing metabolism and achieving long-term health goals.
III. Conclusion
In this article, we have explored the Top 5 Superfoods to Boost Metabolism and that can greatly contribute to a healthy and balanced diet.
A. Encouragement to incorporate these superfoods into daily meals
Incorporating these superfoods into your daily meals can have a profound impact on your overall health and well-being.
While each superfood provides its unique set of benefits, their collective power lies in their ability to provide a wide range of essential nutrients, antioxidants, and healthy fats.
To incorporate these superfoods into your diet, here are a few practical tips
1. Start your day with a blueberry and chia seed smoothie or add them to your oatmeal for a nutritious breakfast.
2. Make kale a staple in your salads or sauté it with other vegetables as a side dish.
3. Substitute quinoa for rice or pasta in your meals to increase your protein intake and add variety.
4. Include salmon in your diet at least twice a week by grilling, baking, or steaming it. Pair it with a side of roasted vegetables or a quinoa salad for a complete meal.
5. Sprinkle chia seeds on top of yogurt, cereal, or add them to your baked goods like muffins or energy bars.
B. Importance of variety and moderation in diet for overall well-being
While incorporating superfoods into your diet is a great step towards a healthy lifestyle, it’s essential to remember that no single food can provide all the necessary nutrients your body needs.
Variety is key to ensure you’re getting a wide range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Additionally, practicing moderation is crucial. Even superfoods should be consumed in appropriate portions to maintain a balanced diet.
IV. Quick Recap of Top 5 Superfoods to Boost Metabolism
- Blueberries
- Kale
- Quinoa
- Salmon
- Chia seeds
A well-rounded approach that includes whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats alongside superfoods will help ensure optimal nutrition.
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making any significant changes to your diet, especially if you have specific dietary requirements or health conditions.
By incorporating these top 5 superfoods into your daily meals, along with a variety of other nutritious foods, you’ll be on your way to achieving a healthy and balanced diet, supporting your overall well-being.
V. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is metabolism, and why is it important?
Metabolism refers to the processes that the body uses to convert food into energy. It plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health, influencing weight management, and supporting various bodily functions.
How do blueberries contribute to boosting metabolism?
Blueberries are rich in antioxidants, particularly anthocyanins, which may have a positive impact on metabolism. Additionally, their fiber content supports digestive health, contributing to an efficient metabolism.
What makes kale a superfood for metabolism?
Kale is a nutrient-dense leafy green with high fiber content, aiding digestion and supporting metabolism. Its diverse range of vitamins and minerals also contributes to overall metabolic health.
How does quinoa support metabolism?
Quinoa is a complete protein source, providing essential amino acids that support muscle health and metabolic function. Its fiber and complex carbohydrates contribute to sustained energy levels.
What sets salmon apart as a metabolism-boosting superfood?
Salmon is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, promoting metabolic health and supporting weight management. Its high-quality protein content also plays a role in boosting metabolism.
How do chia seeds aid in metabolism?
Chia seeds are packed with omega-3 fatty acids and fiber, promoting a feeling of fullness and supporting digestive health. The gel-forming property aids in efficient nutrient absorption and metabolism.
Can I combine these superfoods for better results?
Yes, combining a variety of superfoods can provide a synergistic effect, offering a broader range of nutrients and benefits for overall health and metabolism.
Are there specific recipes to include these superfoods in my diet?
Absolutely! Incorporate blueberries into smoothies, make kale salads, prepare quinoa bowls, enjoy grilled salmon, and add chia seeds to yogurt or oatmeal for delicious and nutritious meals.
How quickly can I expect to see results in my metabolism?
Metabolic changes vary among individuals. Consistency is key, so adopting a long-term approach to a balanced diet and regular exercise will yield more sustainable results.
Can these superfoods replace the need for exercise?
While superfoods contribute to metabolic health, they should complement—not replace—regular physical activity. Both elements work together to achieve and maintain optimal overall health.