India stands at the cusp of a historic economic transformation. As the country approaches its centenary of independence in 2047, the government has set an ambitious goal of achieving sustained annual growth of 8%. According to the Finance Ministry, this vision is not just about numbers; it’s about lifting millions out of poverty, creating opportunities for a young workforce, and placing India firmly among the world’s top economies.
The Finance Ministry’s strategy emphasizes structural reforms, investment in infrastructure, and tapping into global opportunities while mitigating external risks. This forward-looking plan aims to ensure that India not only grows faster but also grows inclusively, empowering every section of society.
Below, we explore the Top 5 reasons why India is charging toward 8% growth by 2047, supported by key policy actions, investment goals, and risk assessments.
1. Finance Ministry’s Strategy for Sustainable Growth

Key Features:
- Long-term policy roadmap for economic stability.
- Focus on structural reforms across key sectors.
- Strong push toward digital transformation and financial inclusion.
- Targeting productivity-driven growth over consumption-led expansion.
- Building resilience against global financial shocks.
The Finance Ministry has laid out a comprehensive strategy to guide India toward its 2047 economic goals. Central to this plan is the shift from short-term stimulus to long-term sustainable growth measures. Structural reforms in agriculture, manufacturing, and services aim to increase productivity while ensuring fair distribution of resources.
Digital transformation and financial inclusion stand at the heart of this plan. With platforms like UPI revolutionizing transactions, India is creating a strong digital backbone for future economic activity. By ensuring that even the most remote regions are financially connected, the government is fostering a more inclusive economy.
Moreover, the ministry’s emphasis on stability and resilience highlights the intent to insulate India from global shocks, whether in the form of recessions, oil price volatility, or geopolitical risks. This steady approach ensures that India’s path to 8% growth remains sustainable.
2. Massive Infrastructure Investment Goals
Key Features:
- Trillions of rupees allocated for roads, railways, and ports.
- Green energy and renewable infrastructure expansion.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) to mobilize capital.
- Focus on smart cities and urbanization.
- Logistics efficiency to cut business costs.
Infrastructure is the backbone of economic growth, and India is pushing massive investments into this sector. From highways to high-speed rail networks, the government is modernizing transport to ensure faster and cheaper movement of goods and people.
The emphasis on renewable energy is equally critical. With the goal of becoming a net-zero nation by 2070, investments in solar, wind, and green hydrogen are setting the stage for energy independence. Public-Private Partnerships are expected to mobilize trillions of rupees in funding, boosting efficiency and innovation.
Smart city projects, digital infrastructure, and urban housing are being scaled up to support rapid urbanization. Improved logistics and reduced transport bottlenecks will further help industries cut costs and improve competitiveness.
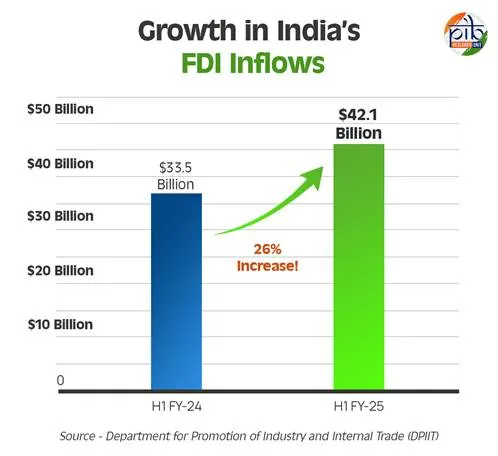
3. Rising Private and Foreign Investments
Key Features:
- India as a hub for global supply chains.
- Stable regulatory environment attracting investors.
- Growth in startup ecosystem and venture capital inflows.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) liberalization in key sectors.
- Manufacturing push under “Make in India” and PLI schemes.
India’s investment climate is rapidly evolving. The government has liberalized Foreign Direct Investment rules in critical sectors like defense, telecom, and retail. This has positioned India as a lucrative destination for global investors looking to diversify away from overdependence on China.
The Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes are boosting manufacturing in electronics, semiconductors, and pharmaceuticals. This not only strengthens domestic supply chains but also makes India a competitive global player.
Meanwhile, the startup ecosystem is booming. With record venture capital inflows and a growing unicorn base, India’s innovation-driven economy is setting benchmarks globally. These investment flows are fueling job creation, technology advancement, and export growth.
4. Harnessing Demographic Dividend and Skilled Workforce
Key Features:
- Young workforce with a median age of 28.
- Large pool of engineers, IT professionals, and skilled labor.
- National Education Policy (NEP) for skill development.
- Training initiatives for Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Expanding women’s participation in the workforce.
India’s demographic dividend is one of its biggest strengths. With over 65% of the population under 35, India has a young and energetic workforce ready to drive innovation and productivity. This contrasts with aging populations in many developed economies, giving India a long-term advantage.
The government’s focus on education and skill development is ensuring that this workforce is industry-ready. Programs aligned with Industry 4.0 – such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and automation – are equipping the next generation with future-ready skills.
Additionally, increasing women’s participation in the labor force is expected to add significantly to GDP growth. By unlocking this untapped potential, India can ensure more inclusive and broad-based development.
5. Managing External Risks and Global Integration
Key Features:
- Diversification of trade partnerships.
- Strengthening regional and global trade alliances.
- Energy security strategies to reduce import dependence.
- Building forex reserves as a cushion against volatility.
- Policy measures to counter global inflation and currency fluctuations.
While opportunities abound, India’s growth path is not without challenges. External risks such as geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions, and global financial instability pose serious threats. Recognizing this, the Finance Ministry has crafted policies to strengthen India’s global integration while minimizing vulnerabilities.
India is diversifying its trade partners to avoid overdependence on any single country. The government is also enhancing energy security by expanding domestic production and building strategic reserves. At the same time, maintaining healthy foreign exchange reserves provides a cushion against currency shocks.
By balancing global integration with risk management, India is ensuring that external factors do not derail its long-term growth trajectory.
Conclusion – Top 5 Reasons Why India is Charging Toward 8% Growth by 2047

India’s journey toward 8% growth by 2047 is driven by a combination of well-structured strategies, bold investment goals, and a focus on resilience. From infrastructure development and foreign investments to leveraging its young workforce and managing external risks, the country is laying a strong foundation for future prosperity.
The Finance Ministry’s plan reflects a balance between ambition and realism. By ensuring sustainability, inclusivity, and adaptability, India is positioning itself as a leading economic power in the coming decades. If these strategies are executed effectively, India is not just aiming for numbers—it is preparing for a transformative growth story that will redefine its global standing.
Table: Key Details of India’s Growth Roadmap
| Factor | Key Highlights | Role in Achieving 8% Growth by 2047 |
|---|---|---|
| Finance Ministry’s Strategy | Structural reforms, digital inclusion, resilience planning | Provides sustainable policy framework |
| Infrastructure Investment | Roads, railways, ports, smart cities, renewable energy | Boosts productivity and lowers costs |
| Investments | FDI liberalization, PLI schemes, startups | Fuels innovation and manufacturing |
| Demographic Dividend | Young workforce, education reforms, women participation | Expands skilled labor pool |
| External Risk Management | Trade diversification, forex reserves, energy security | Protects growth from global shocks |
FAQs on Top 5 Reasons Why India is Charging Toward 8% Growth by 2047
1. Why has India set an 8% growth target by 2047?
India aims to achieve high growth to become a developed nation by its centenary of independence.
2. What role does the Finance Ministry play in this growth?
The Finance Ministry provides policy direction, reforms, and strategies to ensure sustainable and inclusive growth.
3. How important is infrastructure investment for India’s growth?
It is crucial, as modern infrastructure reduces costs, boosts productivity, and attracts investments.
4. What is the significance of the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme?
The PLI scheme boosts manufacturing competitiveness and strengthens supply chains.
5. How does India plan to use its young workforce?
Through skill development, education reforms, and creating jobs in emerging industries.
6. What risks could derail India’s 8% growth target?
Geopolitical tensions, energy price volatility, and global recessions are major risks.
7. How is India diversifying its trade relations?
By building stronger partnerships with multiple regions including Africa, Europe, and Southeast Asia.
8. What role do startups play in India’s growth journey?
Startups drive innovation, job creation, and attract global venture capital.
9. How does renewable energy investment impact growth?
It ensures energy independence, reduces import bills, and supports sustainable development.
10. Can India realistically achieve 8% growth by 2047?
Yes, if current strategies are effectively implemented and external risks are managed.