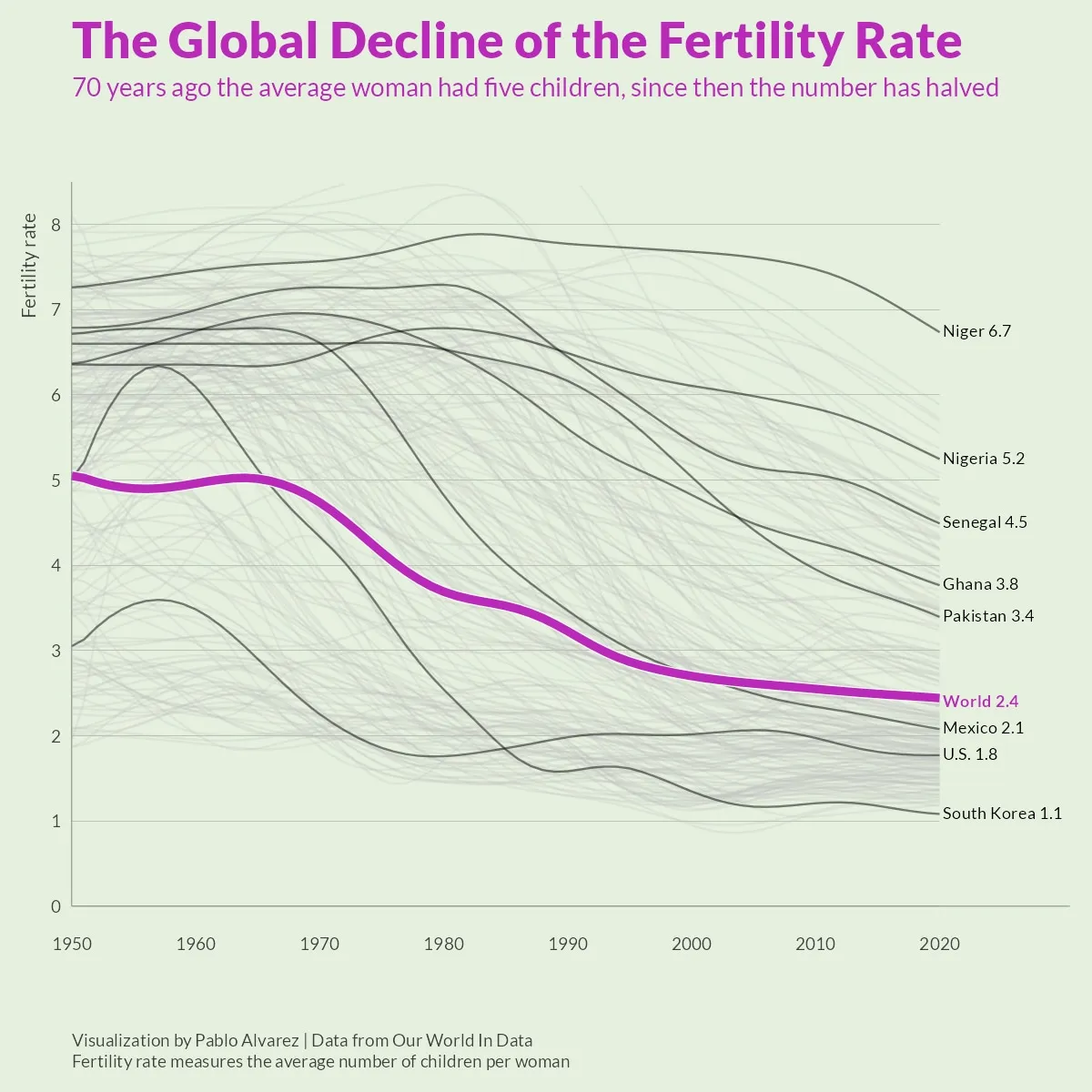
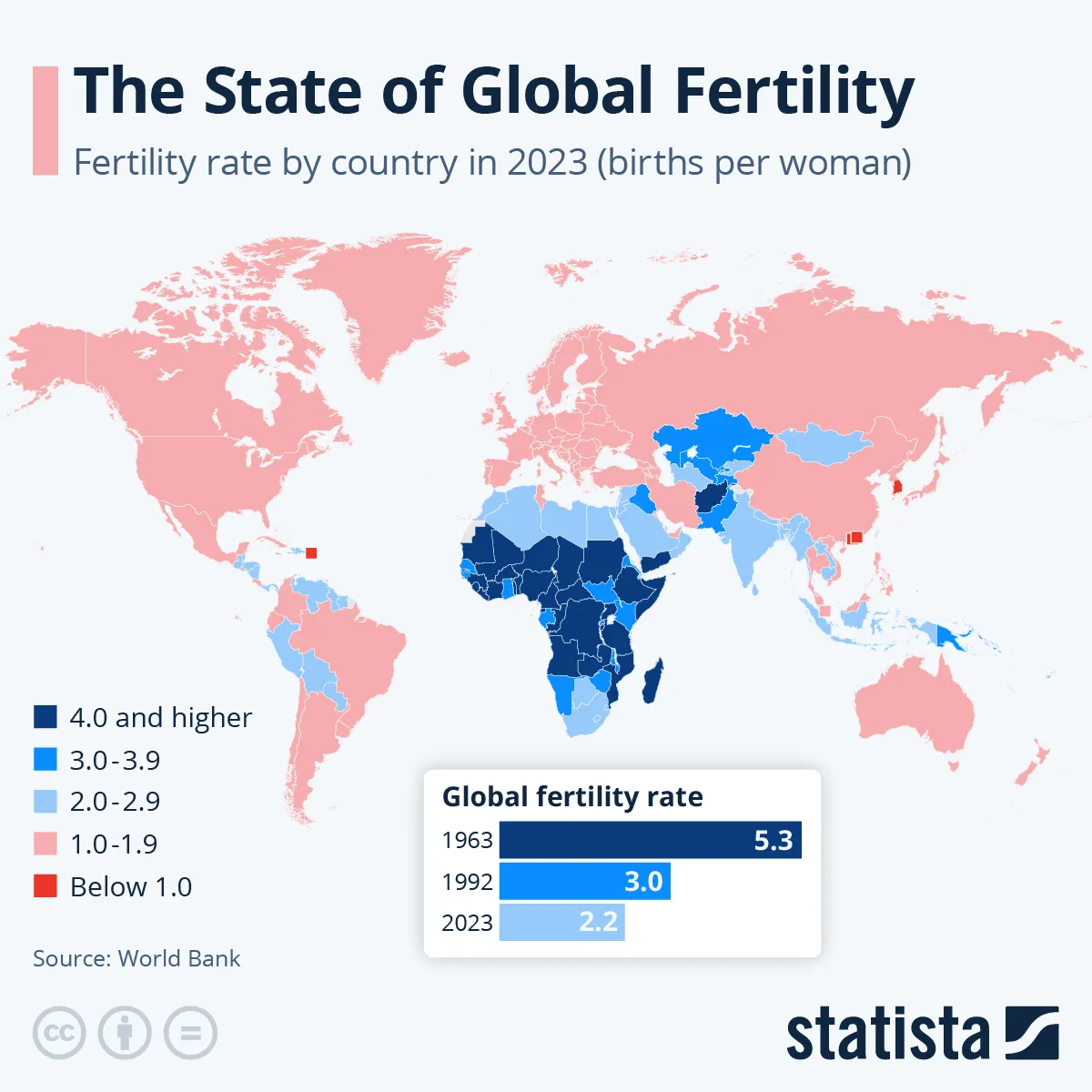
In recent years, the topic of declining birth rates has become one of the most widely discussed global issues. Economists, policymakers, and researchers are raising concerns about why global birth rates are falling faster than expected. This phenomenon is not limited to developed nations but is also visible in developing countries, where traditionally higher fertility rates are now rapidly declining.
The reasons behind this trend are complex and multi-dimensional. From economic stress to shifting cultural values, from the rise of education to advanced healthcare access, the global fertility landscape is changing at an unprecedented pace. Understanding the top 5 reasons global birth rates are falling faster than expected is crucial for governments, families, and future generations.
In this article, we will explore the main causes, explain their impact, and provide insights into how societies are adapting. By the end, you will have a clear understanding of why fertility decline is accelerating and what it means for the future of population growth.
1. Economic Pressures and Rising Cost of Living
Key Features:
- High housing costs discourage young couples from starting families.
- Childcare expenses have become unaffordable in many countries.
- Job insecurity makes long-term planning difficult.
- Women and men delay marriage due to financial instability.
Economic challenges are one of the leading reasons global birth rates are falling faster than expected. The cost of living in urban areas has skyrocketed, with housing, food, healthcare, and education becoming increasingly expensive. Many couples feel financially unprepared to raise children, leading to delayed family planning or the decision not to have children at all.
In addition, job insecurity plays a vital role. In many nations, unstable employment and low wages make it difficult for young adults to invest in family life. Couples who once planned to have two or three children are now settling for one or none. As the cost of raising a child continues to rise, economic stress will remain a key factor in declining global birth rates.
2. Increased Female Education and Workforce Participation
Key Features:
- Higher education empowers women to pursue careers before family.
- Women now prioritize professional success over early motherhood.
- Access to reproductive choices leads to delayed childbirth.
- Gender equality movements shift traditional family roles.
One of the most transformative social changes worldwide has been the rise of female education. Women now have greater access to universities and career opportunities, which significantly alters family planning decisions. When women pursue higher education, they often delay marriage and childbearing to establish careers and achieve financial independence.
This shift has been further strengthened by improved reproductive health services. Women today have more control over when and how many children to have. As societies continue to promote gender equality, traditional expectations of early motherhood are fading, directly contributing to falling global birth rates.
3. Urbanization and Lifestyle Changes
Key Features:
- Urban life encourages smaller families due to space constraints.
- Fast-paced lifestyles reduce time for raising children.
- Access to modern healthcare reduces the need for larger families.
- Increased focus on personal freedom and self-fulfillment.
Urbanization has rapidly transformed family structures around the world. In large cities, limited living space and high property prices discourage larger families. Couples often prefer having one child—or none—because raising children in urban environments is both costly and demanding.
Lifestyle preferences also play a critical role. Today’s generation values independence, travel, career growth, and personal freedom. As a result, fewer people are willing to make the long-term commitment of raising children. This change in priorities reflects a cultural shift that accelerates the decline in global birth rates.
4. Healthcare Advances and Declining Infant Mortality
Key Features:
- Improved healthcare reduces the need for larger families.
- Vaccinations and better nutrition increase child survival rates.
- Family planning services allow couples to limit pregnancies.
- Longer life expectancy changes family priorities.
Another reason global birth rates are falling faster than expected is the advancement of healthcare systems. In earlier generations, parents often had many children due to high infant mortality rates. However, with improved medical care, most children now survive into adulthood, reducing the need for large families.
Family planning and access to contraception also empower couples to make informed decisions about their fertility. As child survival becomes more secure, families are content with having fewer children, contributing to a rapid global fertility decline.
5. Cultural Shifts and Changing Social Norms
Key Features:
- Marriage is being delayed or avoided in many societies.
- Parenthood is no longer seen as a life necessity.
- Rising individualism reduces family-centered living.
- Social acceptance of child-free lifestyles is growing.
Cultural changes have played a massive role in shaping birth rate trends. In the past, having children was considered an essential milestone of adulthood. Today, cultural attitudes are shifting, with many people embracing alternative lifestyles that do not revolve around family building.
Marriage, once the foundation of family life, is also being postponed. More individuals are choosing to remain single or enter into non-traditional partnerships, which often results in fewer children. As societal values continue to evolve, the choice of having fewer or no children has gained broader acceptance, accelerating the decline of global birth rates.
Conclusion – Top 5 Reasons Global Birth Rates Are Falling Faster Than Expected

The question of why global birth rates are falling faster than expected is deeply rooted in economic, social, and cultural transformations. Rising living costs, the empowerment of women, urbanization, healthcare progress, and shifting cultural values are reshaping how individuals and societies view family life.
While some may see this as a challenge, others believe it offers opportunities for sustainable development and improved quality of life. Governments, however, must balance the potential economic consequences of shrinking populations, such as workforce shortages and aging societies.
Ultimately, the global fertility decline is not merely a temporary trend—it is a long-term shift that will define the future of nations. Understanding the top 5 reasons behind falling birth rates helps policymakers and families navigate this demographic transformation more effectively.
Table: Top 5 Reasons Global Birth Rates Are Falling Faster Than Expected
| Reason | Key Features | Impact on Global Birth Rates |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Pressures | High living costs, job insecurity, childcare expenses | Couples delay or avoid having children |
| Female Education & Workforce | Career focus, reproductive choices, gender equality | Women delay childbirth, smaller families |
| Urbanization & Lifestyle | Space limits, fast-paced lives, self-fulfillment | Decline in larger family structures |
| Healthcare Advances | Lower infant mortality, family planning, life expectancy | Reduced need for multiple children |
| Cultural Shifts | Delayed marriage, child-free lifestyle acceptance | Parenthood seen as optional |
FAQs on Top 5 Reasons Global Birth Rates Are Falling Faster Than Expected
1. Why are global birth rates falling faster than expected?
Global birth rates are declining due to economic pressures, women’s education, urbanization, healthcare advances, and changing cultural values.
2. How does the cost of living affect birth rates?
High housing, childcare, and education costs make many couples feel financially unprepared for children, leading to delayed or fewer births.
3. What role does women’s education play in declining birth rates?
Higher education encourages women to focus on careers, financial independence, and delayed family planning, reducing overall fertility rates.
4. How has urbanization influenced family sizes?
Urban living often means higher expenses and less living space, which discourages larger families and promotes smaller households.
5. Why does improved healthcare reduce birth rates?
With lower infant mortality and access to contraception, families no longer need large numbers of children for survival security.
6. Are cultural changes affecting global fertility?
Yes, shifting values around marriage, independence, and child-free lifestyles reduce the pressure to have children.
7. Do economic crises accelerate fertility decline?
Yes, during financial instability, many couples postpone or avoid having children, contributing to declining birth rates.
8. Which regions are experiencing the fastest fertility decline?
Both developed nations and emerging economies, such as South Korea, Japan, Italy, and even parts of India, show rapid declines.
9. What are the long-term consequences of falling birth rates?
A shrinking workforce, aging population, and economic slowdown are major challenges linked to declining birth rates.
10. Can government policies reverse falling birth rates?
Some nations are introducing incentives like childcare support, parental leave, and tax benefits, but reversing the trend remains difficult.