The growing tariff tensions between the United States and India have become a central topic of global trade discussions. Recently, the United States imposed up to 50% tariffs on several key Indian exports, sparking concerns across industries, policy circles, and households. For India, which has long considered the US as one of its top trading partners, these tariffs bring both immediate challenges and long-term uncertainties.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has raised concerns about the potential impact on inflation, currency stability, and growth outlook. At the same time, Indian exporters, manufacturers, and investors are grappling with the new reality of trade restrictions. This article explores the 5 big effects of the US-India tariff tensions on India’s economy, highlighting how they influence exports, investments, inflation, and overall growth prospects.
By examining these critical areas, we can better understand how tariff battles between two of the world’s largest democracies might reshape India’s economic path in the coming years.
1. Impact on India’s Export Sector
Key Features:
- High tariffs on textiles, steel, and pharmaceutical products.
- Reduced competitiveness of Indian goods in the US market.
- Potential diversification toward alternative export markets.
- Short-term revenue losses for Indian exporters.
- Long-term push for trade policy reforms.
India’s export sector is one of the first casualties of the tariff tensions. With the US imposing tariffs as high as 50% on certain Indian goods, industries such as textiles, steel, and pharmaceuticals face serious hurdles. These higher costs make Indian products less competitive compared to those from other emerging economies like Vietnam or Mexico.
Exporters are also struggling to maintain profit margins as they absorb part of the tariff burden. Some have started looking toward new markets in Europe, Africa, and Asia to reduce dependence on the US. While diversification could strengthen India’s long-term trade resilience, the immediate losses in revenue and market share are difficult to ignore.
2. Rising Inflation and RBI Concerns
Key Features:
- Increased import costs for raw materials and machinery.
- Ripple effect on consumer prices in India.
- RBI’s concerns about inflationary pressures.
- Possible policy interventions through interest rates.
- Risk of currency volatility due to trade imbalance.
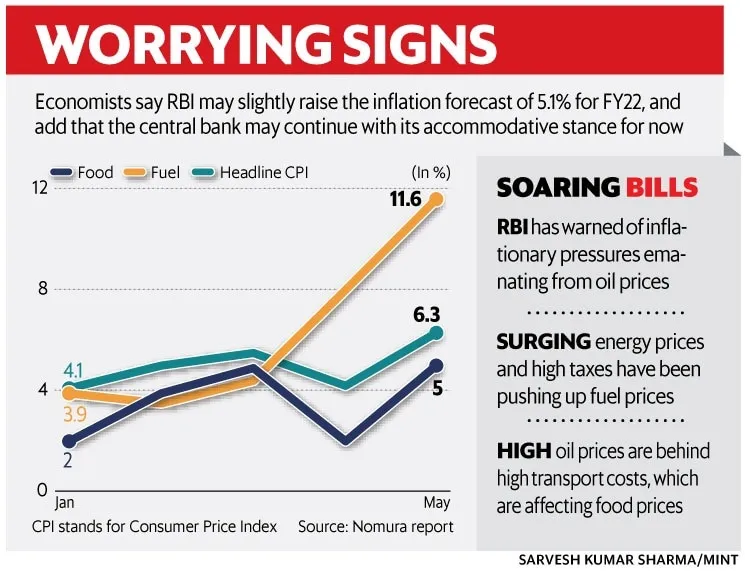
The Reserve Bank of India has voiced concerns that tariff tensions could fuel inflation. Since many Indian industries rely on imported raw materials and machinery, higher tariffs often increase production costs. These costs are eventually passed on to consumers, leading to a rise in food, clothing, and household goods prices.
The RBI faces a balancing act—on one hand, it must keep inflation under control, while on the other, it cannot choke economic growth by raising interest rates too aggressively. The rupee may also come under pressure as trade imbalances widen, forcing the central bank to intervene in currency markets more frequently.
3. Strain on India’s Growth Outlook
Key Features:
- Slower export growth dampens GDP prospects.
- Tariff uncertainty reduces foreign investment flows.
- Risk of job losses in labor-intensive industries.
- Supply chain disruptions in manufacturing.
- Government stimulus may be required to stabilize growth.
India’s economic growth outlook is closely tied to trade performance, investment inflows, and consumer confidence. With tariff tensions weighing on exports and industrial activity, GDP growth projections may face downward revisions. The IMF and World Bank have already cautioned that prolonged tariff disputes could shave off up to 0.5% from India’s growth rate.
Labor-intensive industries such as textiles, leather, and handicrafts may see layoffs, impacting millions of workers. Meanwhile, multinational companies might delay investments in India until trade clarity returns. To counter these challenges, the Indian government may introduce targeted stimulus packages, but fiscal space remains limited.
4. Pressure on Bilateral Trade Relations
Key Features:
- US is India’s top export destination.
- Diplomatic negotiations ongoing to ease tensions.
- Risk of retaliatory tariffs by India.
- Strained partnerships in strategic sectors like defense and technology.
- Long-term need for balanced trade agreements.
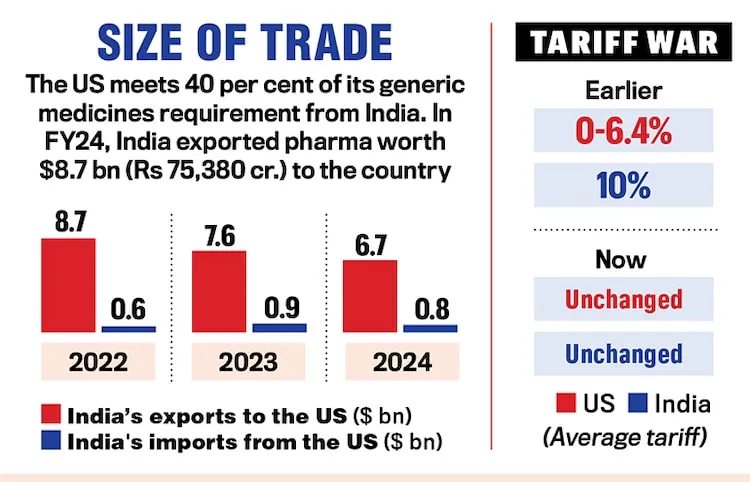
The US accounts for nearly 18% of India’s total exports, making it a critical trade partner. The imposition of steep tariffs has strained bilateral ties, pushing both nations into a delicate negotiation phase. While India has explored retaliatory measures, such as duties on American agricultural products, policymakers are cautious not to escalate the trade war further.
The tensions also affect broader partnerships in defense, digital technology, and climate cooperation. Experts argue that a balanced trade agreement that protects both sides’ interests is the only way forward. Until then, India will continue to walk a fine line between protecting its exporters and maintaining diplomatic ties.
5. Push for Domestic Manufacturing and Self-Reliance
Key Features:
- Boost for the ‘Make in India’ initiative.
- Reduced dependence on foreign markets.
- Incentives for domestic production and supply chains.
- Growth of SMEs (small and medium enterprises).
- Strategic focus on Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India).
While tariff tensions bring immediate difficulties, they also create opportunities for India to strengthen its domestic economy. The government has been promoting self-reliance through initiatives like “Make in India” and “Atmanirbhar Bharat.” With reduced access to foreign markets, Indian industries may focus more on building local manufacturing capacity.
This shift could encourage innovation, support small and medium enterprises, and reduce dependence on imports. However, success will depend on strong policy support, infrastructure development, and long-term investment in technology and skills. If implemented effectively, this could turn a short-term crisis into a long-term advantage for India.
Conclusion – 5 Big Effects of the US-India Tariff Tensions on India’s Economy

The 5 big effects of the US-India tariff tensions on India’s economy reveal a complex mix of challenges and opportunities. From strained exports and inflation risks to long-term manufacturing growth, India is navigating uncertain waters. The RBI’s concerns about inflation, currency stability, and growth underline the seriousness of the situation.
While immediate challenges such as revenue losses, rising costs, and reduced growth prospects cannot be ignored, the tensions may also push India to diversify trade, strengthen domestic industries, and pursue balanced agreements with global partners.
In the long run, how India manages these tensions will determine its path toward sustainable growth, resilience, and self-reliance in the global economy.
Table: Overview of the 5 Big Effects of US-India Tariff Tensions
| Effect | Key Impact | Long-term Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Impact on Exports | Loss of competitiveness, reduced US market share | Push for export diversification |
| Rising Inflation | Higher costs, consumer price rise | RBI interventions, currency stability concerns |
| Strain on Growth | Slower GDP growth, job losses | Government stimulus, cautious investments |
| Bilateral Trade Pressure | Strained US-India relations | Need for balanced trade agreements |
| Domestic Manufacturing Push | Boost to local industries, SMEs | Stronger self-reliant economy |
FAQs on 5 Big Effects of the US-India Tariff Tensions on India’s Economy
1. Why did the US impose 50% tariffs on Indian goods?
The tariffs were imposed due to trade imbalances, market access concerns, and protectionist policies in global trade.
2. How do these tariffs affect Indian exporters?
They reduce competitiveness in the US market, increase costs, and lower profit margins for exporters.
3. What is the RBI’s main concern regarding tariff tensions?
The RBI is concerned about rising inflation, currency instability, and their combined effect on India’s growth outlook.
4. Which Indian industries are most affected by the tariffs?
Textiles, steel, pharmaceuticals, and labor-intensive industries such as handicrafts are among the hardest hit.
5. Could tariff tensions lead to job losses in India?
Yes, especially in export-driven sectors like textiles, leather, and small-scale manufacturing.
6. How might India respond to US tariffs?
India may impose retaliatory duties but is more likely to pursue negotiations to avoid a full-blown trade war.
7. Will these tariffs affect India’s GDP growth?
Yes, experts estimate a slowdown in GDP growth by up to 0.5% if tensions persist.
8. Can India reduce dependence on the US market?
Yes, by diversifying exports to Europe, Africa, and Asian countries, though it will take time.
9. What role does the ‘Make in India’ initiative play in this situation?
It promotes domestic manufacturing, helping reduce dependence on imports and foreign markets.
10. What is the long-term outlook for India amid tariff tensions?
While short-term challenges remain, India could emerge stronger with more diversified trade and resilient domestic industries.